i bc27f85be50b71b1 (32 page)
Read i bc27f85be50b71b1 Online
Authors: Unknown
...,
..
Table 1-A. 1. Electrocardiographic (ECC) Characteristics and Causes of Atrial Rhythms
§ g
Name
ECG Characteristics
Common Causes
PT Consideration
'"
m
Supraventricular
Regular rhythm, rate 1 60-250,
�
Rheumatoid heart
May produce palpitations, chest tight
=
Z
tachycatdia
may originate from any location
disease (RHD),
ness, dizziness, anxiety, apprehension,
c
�
above atrioventricular node, can be
mitral valve proweakness; PT would not treat if in
o
paroxysmal (comes and goes withlapse, cor pulmosupraventricular tachycardia until
"
out reason).
nale, digitalis
controlled.
o
'"
wxicity.
�
Atrial flutter
Rhythm can be regular or irregular,
Mitral stenosis,
Signs and sympwms depend on presence or
;;;
atrial rate of 250--350, ventricular
CAD, hyperabsence of heart disease but can lead to
§ r
rate is variable and depends on the
tension.
CHF, palpitations, angina, and syncope
:i!
conduction ratio (atrial:ventricuif cardiac output decreases far enough w
E
lar-i.e., atrial rate 250, ventric
=
reduce myocardial and cerebral blood
ular rate 125; 2:1 classic saw
�
=
flow; PT treatment would depend on toltooth P waves.)
erance to the rhythm.
Atrial fibrilla
Irregular rhythm, atrial has no rate
One of most com
Can produce CHF, syncope secondary to no
tion (A F)
(just quivers) ventricular varies.
monly encoun
"atrial kick"; if new diagnosis, hold PT
tered rhythms,
until medical treatment; if chronic and
CHF, CAD, RHO,
nor in CHF, would treat with caution.
hypertension, cor
pulmonale.

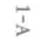
Premature atrial
Irregular rhythm (can be regularly
Normal people with
Usually asympromatic but needs ro be
contractions
irregular, i.e., skip every third
caffeine, smokconsidered with other cardiac issues
beat); rate normal 60-100.
ing, emocional
at time of treatment; can proceed
disturbances;
with treatment with close monitoring;
abnormal with
if they are consistent and increasing
CAD, CHF, eleccan progress [Q AF.
trolyte disturbances.
AF = arrial fibrillation; CAD = coronary artery disease; CHF = congestive heart failure; RHO = rheumatoid heart disease.
Sources; Data from B Aehlert. ACLS Quic.k Review Srudy Guide. St. Louis: Mosby. 1993; and EK Chung. Manual of Cardiac Arrhythmias. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1 986.
2 o " ()
�
-<
� > =ll !Z o x
"
'"

"
Table l-A.2. Electrocardiographic (ECG) Characteristics and Causes of Ventricular Rhythms
'"
>
Name
ECG Characteristics
Common Causes
PT Considerations
�
Agonal rhythm
lrregular rhythm, rate <20,
Near death
Do not creat.
�
no P wave
1::
J:
Ventricular tachycardia
Usually regular rhythm, rate
CAD mosr common after
Do not trear; patiem needs
>
(VT)
> 1 00, no P wave or with
acute Mlj may occur in
immediate medical assis
�
retrograde conduction
rheumatoid hearr disease,
tance; patient may be Stag
and appears after the QRS
cardiomyopathy, hyperble (maimain CO) for
"
complex
tension
shorr while bur can
o
"
progress quickly to unsta
Of
ble (no CO) called pulse
�
less VT.
�
Multifocal VT (rorsades de
Irregular rhythm, rate > 1 50,
Drug induced with antiar
Do nor treat; patiem needs
r
poimes)
no P waves
rhythmic medicines (quiimmediate medical atten
J!
nidine, procainamide)j
tion.
� �
hypokalemia; hypo
�
magnesemia; MI; hypothermia

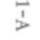
Premature ventricular con
Irregular rhythm, (can be
In normal individuals,
Frequency will dictate effect
tractions (PVCs) (focal
regularly irregular, i.e.,
secondary to caffeine,
on COj need to monitor
=
one ecropic foci and all
skipped beat every fourth
smoking, emotional diselectrocardiograph with
look the same; multifocal
beat); rare varies bur is
turbances; CAD, MI,
treatment; can progress to
more than one ectopic
usually normal 60-100;
cardiomyopathy, MVP,
VTj and this is more likely
=
foci and will have differcouplet is 2 in a row;
digitalis toxicity
if multi focal in nature or
ent wave forms)
bigeminy is every other
if >6 per min; StOp treatbeat; trigeminy is every
ment or rest if change in
third beat
frequency or quality.
Ventricular fibrillation
Chaotic
Severe heart disease mOSt
Needs immediate medical
common after acute MI,
assistance; no PT treathyper- or hypokalemia,
ment.
hypercalcemia, electrocution
Idioventricular rhythm
Essentially regular rhythm,
Advanccd heart diseasc;
CHF is common secondary
rate 20-40
high degree of atriovento slow rateSj hold treat
�
tricular blockj usually a
ment unless rhythm well
;:
terminal arrhythmia
tOlerated.
n
�
CAD = coronary artery disease; CHF = congestive heart failure; CO = cardiac output; MI = myocardial infarction; MVP = micral valve prolapse; vr = ventricular tachycardia.
>
Sources: Data from B Aehlert. ACLS Quick Review Study Guide. St. Louis: Mosby, 1 994; and EK Chung. Manual of Cardiac Arrhythmias.
,.
Boston: Bunerworth-Heinemann, 1986.
� x
'"
'"


