i bc27f85be50b71b1 (80 page)
Read i bc27f85be50b71b1 Online
Authors: Unknown
Sensory and motor input of
Ipsilateral ataxia and
Lateral portion
trunk
discoordination or tremor of
Sensory and motor input of
extremities
extremities for coordination
of gait
Posterior lobe
Medial and lateral portions
Sensory and motor input for
Ipsilateral ataxia and
coordination of motor skills
discoordination of the trunk
and postural tone
Z
m
'"
6
iii
� N '" "


Table 4-2. Continued
N
a..
co
Brain Structure
Substructure
Function
Dysfunction
Flocculonodular
Flocculus nodule
Sensory input from ears
Ipsilateral facial sensory loss
Sensory and motor input from
and Horner's syndrome. nysn
>
eyes and head for coordina�
tagmus, visual overshooting
'"
'"
rion of balance and eye and
Loss of balance
:t
>
head movement
15
1')
ADH
o
= antidiuretic hormone; eN = cranial nerve; ICP = intracranial pressure.
"
Sources; Data from KW Lindsay, I Bone, R Callander (cds). Neurology and Neurosurgery Illustrated (2nd ed). Edinburgh, UK: Churchill Ci
Livingstone, 1991; S Gilman, SW Newman (cds). Manter and Gatz's Essentials of Clinical Neuroanaromy and Neurophysiology (7th ed),
'"
Philadelphia: FA Davis, 1989; JA Kiernan (ed). Introduction to Human Neuroscience. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1987; EN Marieb fed). Human
�
:t
Anatomy and Physiology (5th ed). San Francisco: Benjamin-Cummings. 2001; and L Thelan, J Davie, M Lough reds). Critical Care Nursing:
�
Diagnosis and Managemenr (2nd ed). St. Louis: Mosby. 1994.
o
r
:i
m
s:
�
�


NERVOUS SYSTEM
269
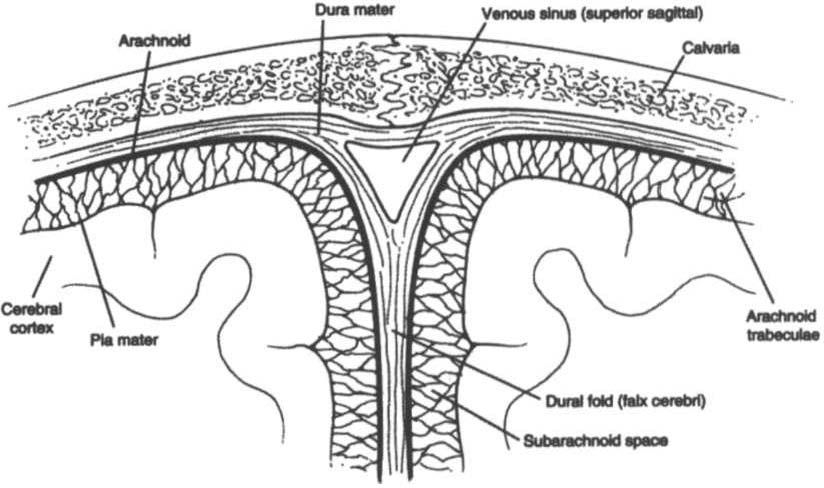
Meninges
The meninges are three layers of connective tissue that cover the brain
and spinal cord. The dura marer, rhe outermost layer, lines the skull
(periosteum) and has four major folds (Table 4-3). The arachnoid, the
middle layer, loosely encloses the brain. The pia mater, the inner layer,
covers the convolutions of the brain and forms a portion of the choroid plexus in the ventricular system. The three layers create very important anatomic and potential spaces in the brain, as shown in
Figure 4-2 and described in Table 4-4.
Ventricular System
The ventricular system nourishes the brain and acts as a cushion
by increasing the buoyancy of the brain. It consists of four ventricles and a series of foramen, through which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) passes to surround rhe CNS. CSF is a colorless, odorless
solution produced by rhe choroid plexus of all ventricles. CSF circulares in a pulse-like fashion through the ventricles and around the spinal cord with the beating of ependymal cilia rhar line the
ventricles and intracranial blood volume changes that occur with
breathing and cardiac systole] The flow of CSF under normal conditions, as shown in Figure 4-3, is as follows4:
Table 4-3. Dural Folds
Falx cerebri
Vertical fold that separates the two cerebral hemi·
spheres ro prevent horizontal displacement of
these structures
Falx cerebelli
Vertical fold that separates the two cerebellar
hemispheres to prevent horizontal displacement
of these structures
Tentorium cerebelli
Horizontal fold that separates occipital lobes from
the cerebellum to prevent vertical displacement
of these Structures
Diaphragm sellae
Horizontal fold that separates that subarachnoid
space from the sella turcica and is perforated by
the stalk of the pituitary gland
Source: Data from JL Wilkinson (ed). Neuroanatomy for Medical Srudents (3rd ed).
Oxford, UK: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1998.


270
AClJTE CARE HANDBOOK FOR PHYSICAL THERAPISTS
Figure 4-2. Coronal section o( cranial meninges showing a venous sinus and
dural (old. ( With permission from PA Young, PH Young. Basic Clinical Nellroallatomy. Phi/adelphia: \Vil/iams & \Vi/kills, 1997;8.)
•
From the lateral ventricles via the interventricular foramen to
the third ventricle
• From the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle via the cerebral
aqueduct
• From the fourth ventricle to the cisterns, subarachnoid space,
and spinal cord via the median and lateral apertures
Table 4-4. Dural Spaces
Epidural (extradural) space
Potential space between the skull and outer
dura mater.
Subdural space
Potential space between [he dura and [he
arachnoid mater; a split in the dura contains the venous sinus.
Subarachnoid space
Anaromic space between the arachnoid and
pia ll1!lter containing cerebrospinal Auid
and the vascular supply of the cortex.
