Power Hungry (10 page)
Authors: Robert Bryce
Although oil has been the undisputed champion, the jockeying for second place has been ferocious. In 1958, natural gas sped past coal to become the second-largest source of primary energy in the United States. Gas kept its second-place status behind oil for nearly two decades, and by 1971, the United States was consuming nearly twice as much energy in the form of natural gas as it was in the form of coal.
3
But Congress and federal regulators decided that the market couldn't be trusted; thanks to
their ham-handed interventions, coal rebounded in a big way. In 1986, coal overtook natural gas to reclaim second place in the U.S. primary energy market. Since then, coal and natural gas have been running neck and neck, with each claiming about 25 percent.
3
But Congress and federal regulators decided that the market couldn't be trusted; thanks to
their ham-handed interventions, coal rebounded in a big way. In 1986, coal overtook natural gas to reclaim second place in the U.S. primary energy market. Since then, coal and natural gas have been running neck and neck, with each claiming about 25 percent.
The decades-long jousting for primacy among the various hydrocarbons provides more evidence of just how difficult it will be to replace them. As Vaclav Smil explained in his 2008 book,
Global Catastrophes and Trends
, there's no reason to expect that the transition toward renewable sources such as solar and wind will be completed quickly. In fact, he says to expect the opposite:
Global Catastrophes and Trends
, there's no reason to expect that the transition toward renewable sources such as solar and wind will be completed quickly. In fact, he says to expect the opposite:
There is no urgency for an accelerated shift to a nonfossil fuel world: the supply of fossil fuels is adequate for generations to come; new energies are not qualitatively superior; and their production will not be substantially cheaper. The plea for an accelerated transition to nonfossil fuels results almost entirely from concerns about global climate change, but we still cannot quantify its magnitude and impact with high confidence.
4
4
Furthermore, the longer we use hydrocarbons, the more entrenched they become in our way of lifeâand the more energy we produce with hydrocarbons, the more energy we are able to produce. That may sound like an exaggeration, but it's a statement that can easily be confirmed by looking back at the history of the coal business. The first railroads were built to haul coal, and the locomotives that hauled the coal also burned coal. As author Jeff Goodell wrote in his book
Big Coal
, the railroads were a key invention that led to more coal production because, “In effect, coal hauled itself.”
5
Of course, the railroads were only part of the equation. By perfecting the steam engine, James Watt enabled British mines to produce coal more economically, because his engines pumped water and lifted coal out of the mines.
6
Big Coal
, the railroads were a key invention that led to more coal production because, “In effect, coal hauled itself.”
5
Of course, the railroads were only part of the equation. By perfecting the steam engine, James Watt enabled British mines to produce coal more economically, because his engines pumped water and lifted coal out of the mines.
6
The idea that hydrocarbons beget more hydrocarbons can also be seen by looking at the Cardinal coal mine in western Kentucky. The mine produces more than 15,000 tons of coal per day. And the essential commodity that facilitates the mine's amazing productivity is electricity. The massive machines that claw the coal from the earth run on electricity
provided by power plants on the surface that burn coal. In fact, about 93 percent of Kentucky's electricity is produced from coal.
7
To paraphrase Goodell, at the Cardinal Mine, the coal, in effect, is mining itself.
provided by power plants on the surface that burn coal. In fact, about 93 percent of Kentucky's electricity is produced from coal.
7
To paraphrase Goodell, at the Cardinal Mine, the coal, in effect, is mining itself.
Hydrocarbons are begetting more hydrocarbons in the oil and gas business. Modern drilling rigs can bore holes that are five, six, or even eight miles long in the quest to tap new reservoirs of oil. And the energy they use to access that oil is ... oil. Diesel fuel has long been the fuel of choice for drilling rigs around the world. On offshore drilling rigs, the power is often supplied by diesel fuel. But in some cases, the power is provided by natural gas that the rig itself produces. Thus, on those offshore platforms, the natural gas is, in effect, mining itself.
The transition away from oil, coal, and natural gas will be a decades-long process because the companies that produce those commodities are getting ever better at finding and exploiting them. The oil and gas industry provides a clear example of this. For about a century, analysts have been forecasting an end to the supply of petroleum. And they have consistently been proven wrong. Why? Because the companies that produce oil and gas continue to discover new ways to gain access to previously inaccessible resources.
Though environmental groups and energy analysts eagerly publicize the inventiveness of entrepreneurs working to improve wind- and solar-power technology and other ways to harness alternative sources of energy, they seldom mention the ongoing innovations that are occurring on the hydrocarbon side of the ledger. And in doing so, they frequently forget the sheer size of the industry that is constantly searching for techniques that can get oil and gas out of the ground and do so faster and cheaper than before.
In the United States, there are about 5,000 independent oil and gas companies, every one of which is continually spending money and testing new concepts that will wring yet more petroleum and natural gas out of their leases.
8
In 2007 alone, those companies spent $226 billion drilling and equipping some 54,300 wells.
9
And that doesn't include the money spent on research and technology. All of the money spent on drilling and outfitting those wells, and the investment those companies have made in research and development, helps to assure that the installed fleet of machinery that supplies us with horsepower will continue to be fueled primarily by hydrocarbons.
8
In 2007 alone, those companies spent $226 billion drilling and equipping some 54,300 wells.
9
And that doesn't include the money spent on research and technology. All of the money spent on drilling and outfitting those wells, and the investment those companies have made in research and development, helps to assure that the installed fleet of machinery that supplies us with horsepower will continue to be fueled primarily by hydrocarbons.
It was only six decades ago that the oil industry drilled its first offshore oil wellâthe Kermac 16âout of the sight of land.
10
And that well was drilled in just 20 feet of water.
11
Today, Anadarko Petroleum is producing natural gas at the Independence Hub in the Gulf of Mexico, where the water depth is 8,000 feet, and that one platform provides enough natural gas to supply about 5 million homes.
12
Moreover, the companies that are drilling for oil around the world are continually pushing into ever-deeper waters. In 2003, Transocean, the world's largest offshore drilling contractor, announced that it had drilled a well in 10,000 feet of water.
13
Five years later, the firm announced that it had drilled a well off the coast of Qatar with a horizontal section that extended some 6.7 miles. The total measured depth of the well was 40,320 feet (7.6 miles), making it the longest extended-reach well ever drilled.
14
But that record will almost certainly be eclipsed in the next few years, as Houston-based Parker Drilling has recently completed the design and construction of a rig that will be capable of extended-reach wells with lengths of up to 44,000 feet, or 8.3 miles.
10
And that well was drilled in just 20 feet of water.
11
Today, Anadarko Petroleum is producing natural gas at the Independence Hub in the Gulf of Mexico, where the water depth is 8,000 feet, and that one platform provides enough natural gas to supply about 5 million homes.
12
Moreover, the companies that are drilling for oil around the world are continually pushing into ever-deeper waters. In 2003, Transocean, the world's largest offshore drilling contractor, announced that it had drilled a well in 10,000 feet of water.
13
Five years later, the firm announced that it had drilled a well off the coast of Qatar with a horizontal section that extended some 6.7 miles. The total measured depth of the well was 40,320 feet (7.6 miles), making it the longest extended-reach well ever drilled.
14
But that record will almost certainly be eclipsed in the next few years, as Houston-based Parker Drilling has recently completed the design and construction of a rig that will be capable of extended-reach wells with lengths of up to 44,000 feet, or 8.3 miles.
Conceiving of an 8-mile-long well boggles the mind, particularly when you learn that the Daisy Bradford No. 3, the well that started the flood of oil development in the East Texas Field, was only 3,500 feet deep.
15
By drilling deeper and faster, and in locations that were previously thought to be uneconomic, the oil and gas industry has continually extended its life expectancy.
15
By drilling deeper and faster, and in locations that were previously thought to be uneconomic, the oil and gas industry has continually extended its life expectancy.
In the natural gas sector, recent breakthroughs in shale gas technology have unlocked vast quantities of methane. Over the past five years, U.S. shale gas production has soared, thanks to techniques such as micro-seismic analysis, horizontal drilling, and enhanced well completion. The ever-increasing use of technology in the oil and gas business has resulted in huge improvements in drilling success rates. For instance, the success rate today for “wildcats” (wells drilled in frontier areas) is 50 percent or better. Three decades ago, that success rate was about 10 percent.
16
16
While the oil and gas industry continues to improve the techniques that allow companies to drill wells deeper, faster, with greater precision, at ever-lower costs, the coal industry continues to show its resilience. Although oil passed coal as the most important source of U.S. energy
back in 1950, coal hasn't gone away. In fact, over the past few years, thanks to soaring global demand for electricity, coal has enjoyed a resurgence. Although we now live in the Age of Oil, the Age of Coal hasn't yet passed. The reason for coal's enduring popularity is that it provides huge quantities of the essential commodity of modernity: electricity.
back in 1950, coal hasn't gone away. In fact, over the past few years, thanks to soaring global demand for electricity, coal has enjoyed a resurgence. Although we now live in the Age of Oil, the Age of Coal hasn't yet passed. The reason for coal's enduring popularity is that it provides huge quantities of the essential commodity of modernity: electricity.
Over the past two decades, global electricity consumption has grown faster than any other type of energy use, and since 1990 electricity use has increased nearly three times as fast as oil consumption. In their thoughtful 2005 book,
The Bottomless Well
, Peter Huber and Mark Mills declared that “economic growth marches hand in hand with increased consumption of electricityâalways, everywhere, without significant exception in the annals of modern industrial history.”
17
The Bottomless Well
, Peter Huber and Mark Mills declared that “economic growth marches hand in hand with increased consumption of electricityâalways, everywhere, without significant exception in the annals of modern industrial history.”
17
Electricity is the energy commodity that separates the developed countries from the rest. Countries that can provide cheap and reliable electric power to their citizens can grow their economies and create wealth. Those that can't, can't. The essentiality of electricity takes us back to coal. Love it or hate it, coal provides the cheapest option for electricity generation in dozens of countries around the world, and in heavily populated developing countries such as China, India, and Indonesiaâall of which have large coal depositsâthe need for increased capacity for the generation of electricity is acute.
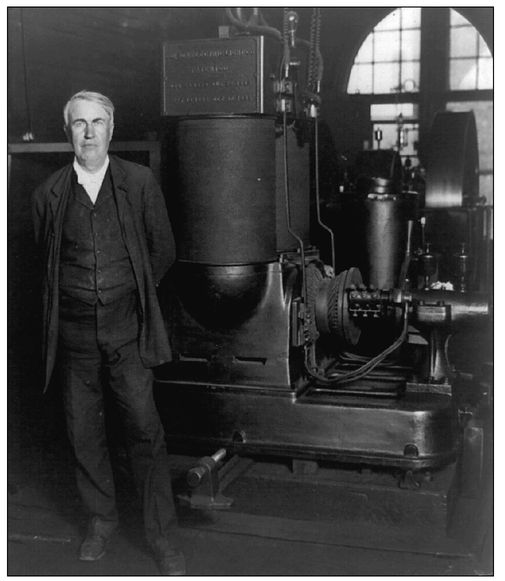
Nearly 130 years ago, Thomas Edison began electrifying the world by burning coalâand in the intervening century, not much has changed.
CHAPTER 5
Coal Hard Facts
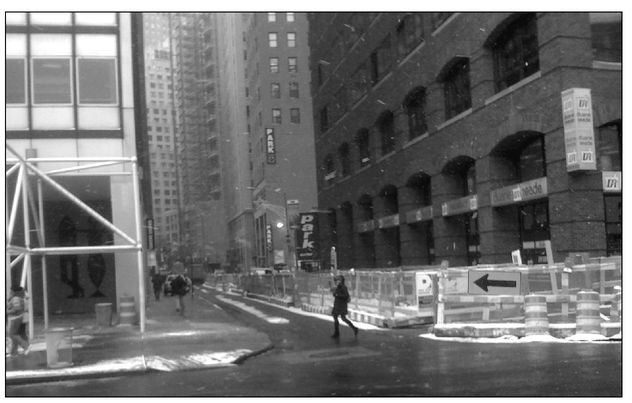

PHOTO 3
A cold day at 255â257 Pearl Street, New York City, January 15, 2009
A cold day at 255â257 Pearl Street, New York City, January 15, 2009
T
HE BEGINNING OF the modern world can be traced to a single address: 255â257 Pearl Street, New York City.
HE BEGINNING OF the modern world can be traced to a single address: 255â257 Pearl Street, New York City.
Modern visitors to that address, located just a block or two west of the entrance to the tourist attractions at South Street Seaport, are unlikely to be impressed. The ground floor of the red brick high-rise building that now occupies the site is dominated by a Duane Reade drugstore. Aside from a bronze plaque mounted on the outside of the building, there's nothing that tells visitors about the importance of that plot of ground.
And yet, on September 4, 1882, Thomas Edison's operations at 255â257 Pearl Street ignited a revolution that transformed the world. On that date, he and his team of workmen began producing commercial quantities of electricity at the world's first central power station.
And yet, on September 4, 1882, Thomas Edison's operations at 255â257 Pearl Street ignited a revolution that transformed the world. On that date, he and his team of workmen began producing commercial quantities of electricity at the world's first central power station.
Edison chose the Pearl Street site because it was affordable and close to office buildings full of likely customers for his product. He paid about $65,000 for the two buildings, then reinforced the interior of the fourstory structure at 257 Pearl with iron beams so it could hold the weight of six generators, each of which was named “Jumbo.” On the floor below the generators were the boilers. The smaller building at 255 Pearl was used for office space, storage, and sleeping quarters for the workers.
1
The location of the two buildings proved ideal. Within months of starting his business, Edison had 203 customers who were using a total of 3,477 of his incandescent lights. By October 1883, having more than doubled his business, he had 508 customers who were using 10,164 lamps.
2
Edison clearly understood the importance of the Pearl Street endeavor, later calling it “the biggest and most responsible thing I had ever undertaken.... Success meant world-wide adoption of our centralstation plan.”
3
1
The location of the two buildings proved ideal. Within months of starting his business, Edison had 203 customers who were using a total of 3,477 of his incandescent lights. By October 1883, having more than doubled his business, he had 508 customers who were using 10,164 lamps.
2
Edison clearly understood the importance of the Pearl Street endeavor, later calling it “the biggest and most responsible thing I had ever undertaken.... Success meant world-wide adoption of our centralstation plan.”
3
Edison's technological breakthroughs at Pearl Streetâthat list includes not only the incandescent bulb, but also the safety fuse, the light socket, the key switch, the generator, and insulated wiringâled to a tsunami of electrification that continues to this day. By 1890, just eight years after Edison launched the beginning of the new world, there were 1,000 central power stations in the United States, and new ones were being added at a frenzied pace.
4
4
In retrospect, it's remarkable to note just how small and inefficient Edison's Pearl Street station was. In 1882, Edison's state-of-the-art machinery converted less than 2.5 percent of the heat energy in the coal into electricity.
5
For comparison, some modern coal-fired power plants, using “ultra-supercritical” technology, can convert nearly half of the coal's heat energy into electric power.
6
As for its size, the Pearl Street plant was a midget by modern standards. Edison's first power plant produced 600,000 watts, or the equivalent of about 804 horsepower.
7
That's only a bit more output than a 2009 Ferrari 599 GTB Fiorano, which comes screaming out of the factory with a 620-horsepower engine.
8
5
For comparison, some modern coal-fired power plants, using “ultra-supercritical” technology, can convert nearly half of the coal's heat energy into electric power.
6
As for its size, the Pearl Street plant was a midget by modern standards. Edison's first power plant produced 600,000 watts, or the equivalent of about 804 horsepower.
7
That's only a bit more output than a 2009 Ferrari 599 GTB Fiorano, which comes screaming out of the factory with a 620-horsepower engine.
8
Other books
The Penultimate Chance Saloon by Simon Brett
Adrift in the Sound by Kate Campbell
Stormcaller (Book 1) by Everet Martins
Ask the Passengers by A. S. King
The Galaxy Builder by Keith Laumer
The Time Regulation Institute by Ahmet Hamdi Tanpinar
Bloody Mary by Thomas, Ricki
Medium Rare: (Intermix) by Meg Benjamin
Another Perfect Catastrophe by Brad Barkley
Letting Her Lead (Ghost Riders MC Book 3) by Alexa Riley