The Name of the Rose (46 page)
Read The Name of the Rose Online
Authors: Umberto Eco
We tried every position, but with no result. Besides our images, the mirror reflected only hazy outlines of the rest of the room, dimly illuminated by the lamp.
“Then,” William meditated, “by âsupra idolum' he could mean beyond the mirror . . . which would oblige us to go into the next room, for surely this mirror is a door. . . .”
The mirror was taller than a normal man, fixed to the wall by a sturdy oak frame. We touched it in every manner, we tried to thrust our fingers into it, our nails between the frame and the wall, but the mirror was as fast as if it were part of the wall, a stone among stones.
“And if not beyond, it could be âsuper idolum,'” William murmured, and meanwhile raised his arm, stood on tiptoe, and ran his hand along the upper edge of the frame. He found nothing but dust.
“For that matter,” William reflected gloomily, “even if beyond it there were a room, the book we are seeking and the others sought is no longer in that room, because it was taken away, first by Venantius and then, God knows where, by Berengar.”
“But perhaps Berengar brought it back here.”
“No, that evening we were in the library, and everything suggests he died not long after the theft, that same night, in the balneary. Otherwise we would have seen him again the next morning. No matter . . . For the present we have established where the finis Africae is and we have almost all the necessary information for perfecting our map of the library. You must admit that many of the labyrinth's mysteries have now been clarified.”
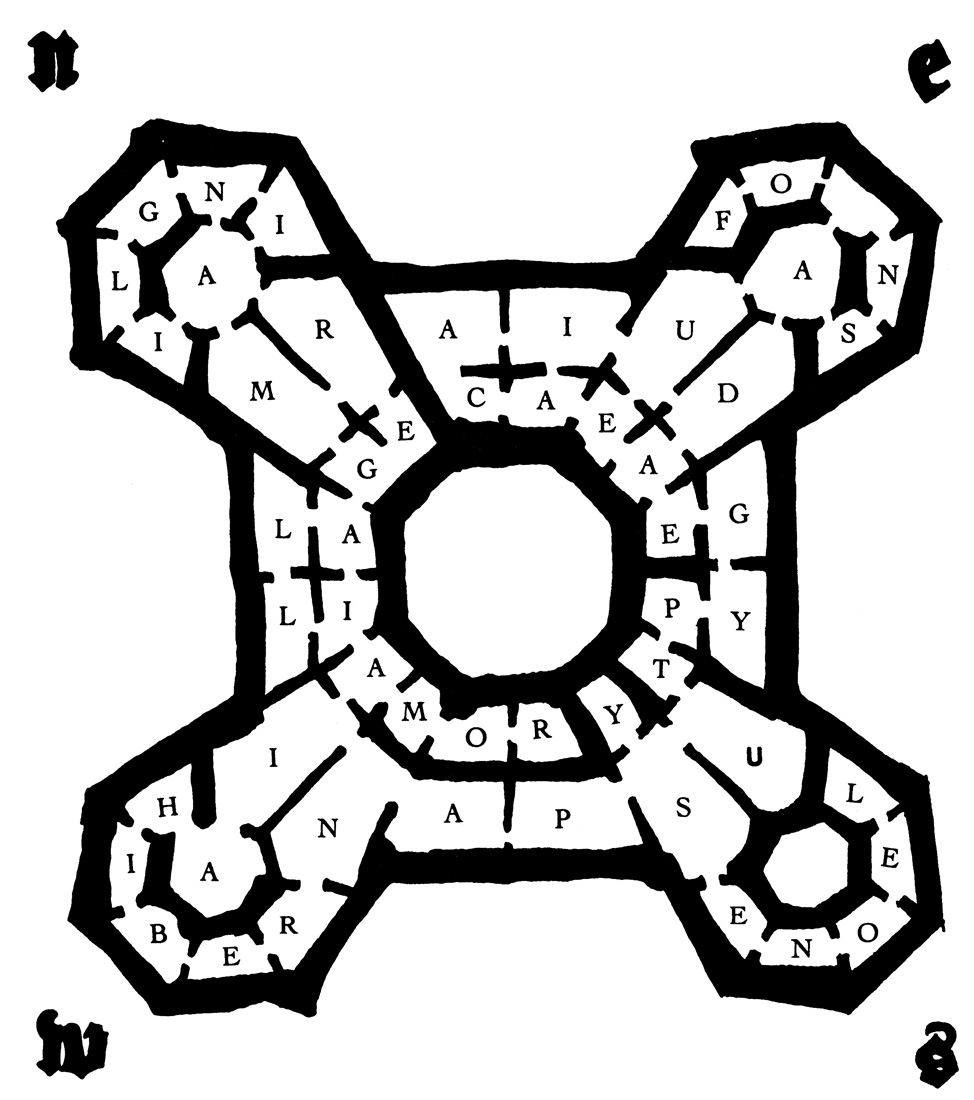
We went through other rooms, recording all our discoveries on my map. We came upon rooms devoted solely to writings on mathematics and astronomy, others with works in Aramaic characters which neither of us knew, others in even less recognizable characters, perhaps texts from India. We moved between two overlapping sequences that said
IUDAEA
and
AEGYPTUS
. In short, not to bore the reader with the chronicle of our deciphering, when we later perfected the map definitively we were convinced that the library was truly laid out and arranged according to the image of the terraqueous orb. To the north we found
ANGLIA
and
GERMANI
, which along the west wall were connected by
GALLIA
, which turned then, at the extreme west, into
HIBERNIA
, and toward the south wall
ROMA
(paradise of Latin classics!) and
YSPANIA
. Then to the south came the
LEONES
and
AEGYPTUS
, which to the east became
IUDAEA
and
FONS ADAE
. Between east and north, along the wall,
ACAIA
, a good synecdoche, as William expressed it, to indicate Greece, and in those four rooms there was, finally, a great hoard of poets and philosophers of pagan antiquity.
The system of words was eccentric. At times it proceeded in a single direction, at other times it went backward, at still others in a circle; often, as I said before, the same letter served to compose two different words (and in these instances the room had one case devoted to one subject and one to another). But obviously there was no point looking for a golden rule in this arrangement. It was purely a mnemonic device to allow the librarian to find a given work. To say of a book that it was found in “quarta Acaiae” meant that it was in the fourth room counting from the one in which the initial
A
appeared, and then, to identify it, presumably the librarian knew by heart the route, circular or straight, that he should follow, as
ACAIA
was distributed over four rooms arranged in a square. So we promptly learned the game of the blank walls. For example, approaching
ACAIA
from the east, you found none of the rooms led to the following rooms: the labyrinth at this point ended, and to reach the north tower you had to pass through the other three. But naturally the librarians entered from the
FONS
, knowing perfectly well that to go, let us say, into
ANGLIA
, they had to pass through
AEGYPTUS
,
YSPANIA
,
GALLIA
, and
GERMANI
.
Â
Â
With these and other fine discoveries our fruitful exploration in the library ended. But before saying that we prepared, contentedly, to leave it (only to be involved in other events I will narrate shortly), I must confess that just as we were moving around the rooms of the south tower, known as
LEONES
, my master happened to stop in a room rich in Arabic works with odd optical drawings; and since we were that evening provided not with one but with two lamps, I moved, in my curiosity, into the next room, realizing that the wisdom and the prudence of the library's planning had assembled along one of its walls books that certainly could not be handed out to anyone to read, because they dealt in various ways with diseases of body and spirit and were almost always written by infidel scholars. And my eye fell on a book, not large but adorned with miniatures far removed (luckily!) from the subject: flowers, vines, animals in pairs, some medicinal herbs. The title was
Speculum amoris,
by Maximus of Bologna, and it included quotations from many other works, all on the malady of love. As the reader will understand, it did not require much once more to inflame my mind, which had been numb since morning, and to excite it again with the girl's image.
All that day I had driven myself to dispel my morning thoughts, repeating that they were not those of a sober, balanced novice, and moreover, since the day's events had been sufficiently rich and intense to distract me, my appetites had been dormant, so that I thought I had freed myself by now from what had been but a passing restlessness. Instead, I had only to see that book to realize I was more sick with love than I had believed. I learned later that, reading books of medicine, you are always convinced you feel the pains of which they speak. So it was that the mere reading of those pages, glanced at hastily in fear that William would enter the room and ask me what I was so diligently investigating, caused me to believe that I was suffering from that very disease, whose symptoms were so splendidly described that if, on the one hand, I was distressed to discover I was sick, on the other I rejoiced to see my own situation depicted so vividly, convincing myself that even if I was sick, my infirmity was, so to speak, normal, inasmuch as countless others had suffered in the same way.
So I was moved by the pages of Ibn-Hazm, who defines love as a rebel illness whose treatment lies within itself, for the sick person does not want to be healed and he who is ill with it is reluctant to get well (and God knows this was true!). I realized why, that morning, I had been so stirred by everything I saw: it seems that love enters through the eyes, as Basil of Ancira also says, andâunmistakable symptomâhe who is seized by such an illness displays an excessive gaiety, while he wishes at the same time to keep to himself and seeks solitude (as I had done that morning), while other phenomena affecting him are a violent restlessness and an awe that makes him speechless. . . .
I was frightened to read that the sincere lover, when denied the sight of the beloved object, must fall into a wasting state that often reaches the point of confining him to bed, and sometimes the malady overpowers the brain, and the subject loses his mind and raves (obviously I had not yet reached that phase, because I had been quite alert in the exploration of the library). But I read with apprehension that if the illness worsens, death can ensue, and I asked myself whether the joy I derived from thinking of the girl was worth this supreme sacrifice of the body, apart from all due consideration of the soul's health.
I learned, further, from some words of Saint Hildegard that the melancholy humor I had felt during the day, which I attributed to a sweet feeling of pain at the girl's absence, was perilously close to the feeling experienced by one who strays from the harmonious and perfect state man experiences in paradise, and this “nigra et amara” melancholy is produced by the breath of the serpent and the influence of the Devil. An idea shared also by infidels of equal wisdom, for my eyes fell on the lines attributed to Abu-Bakr Muhammad ibn-Zakariyya ar-Razi, who in a
Liber continens
identifies amorous melancholy with lycanthropy, which drives its victim to behave like a wolf: first the lovers seem changed in the external appearance, their eyesight weakens, their eyes become hollow and without tears, their tongue slowly dries up and pustules appear on it, the whole body is parched and they suffer constant thirst; at this point they spend the day lying face down, and on the face and the tibias marks like dog bites appear, and finally the victims roam through the cemeteries at night.
Finally, I had no more doubts as to the gravity of my situation when I read quotations from the great Avicenna, who defined love as an assiduous thought of a melancholy nature, born as a result of one's thinking again and again of the features, gestures, or behavior of a person of the opposite sex (with what vivid fidelity had Avicenna described my case!): it does not originate as an illness but is transformed into illness when, remaining unsatisfied, it becomes obsessive thought (and why did I feel so obsessed, I who, God forgive me, had been well satisfied? Or was perhaps what had happened the previous night not satisfaction of love? But how is this illness satisfied, then?), and so there is an incessant flutter of the eyelids, irregular respiration; now the victim laughs, now weeps, and the pulse throbs (and indeed mine throbbed, and my breathing stopped as I read those lines!). Avicenna advised an infallible method already proposed by Galen for discovering whether someone is in love: grasp the wrist of the sufferer and utter many names of members of the opposite sex, until you discover which name makes the pulse accelerate. I was afraid my master would enter abruptly, seize my arm, and observe in the throbbing of my veins my secret, of which I would have been greatly ashamed. . . .
Alas, as remedy Avicenna suggested uniting the two lovers in matrimony, which would cure the illness. Truly he was an infidel, though a shrewd one, because he did not consider the condition of the Benedictine novice, thus condemned never to recoverâor, rather, consecrated, through his own choice or the wise choice of his relatives, never to fall ill. Luckily Avicenna, though not thinking of the Cluniac order, did consider the case of lovers who cannot be joined, and advised as radical treatment hot baths. (Was Berengar trying to be healed of his lovesickness for the dead Adelmo? But could one suffer lovesickness for a being of one's own sex, or was that only bestial lust? And was the night I had spent perhaps not bestial and lustful? No, of course not, I told myself at once, it was most sweetâand then immediately added: No, you are wrong, Adso, it was an illusion of the Devil, it was most bestial, and if you sinned in being a beast you sin all the more now in refusing to acknowledge it!) But then I read, again in Avicenna, that there were also other remedies: for example, enlisting the help of old and expert women who would spend their time denigrating the belovedâand it seems that old women are more expert than men in this task.
Perhaps this was the solution, but I could not find any old women at the abbey (or young ones, actually), and so I would have to ask some monk to speak ill to me of the girl, but who? And besides, could a monk know women as well as an old gossip would know them?
The last solution suggested by the Saracen was truly immodest, for it required the unhappy lover to couple with many slave girls, a remedy quite unsuitable for a monk. And so, I asked myself finally, how can a young monk be healed of love? Is there truly no salvation for him? Should I perhaps turn to Severinus and his herbs? I did find a passage in Arnold of Villanova, an author I had heard William mention with great esteem, who had it that lovesickness was born from an excess of humors and pneuma, when the human organism finds itself in an excess of dampness and heat, because the blood (which produces the generative seed), increasing through excess, produces excess of seed, a “complexio venerea,” and an intense desire for union in man and woman. There is an estimative virtue situated in the dorsal part of the median ventricle of the encephalus (What is that? I wondered) whose purpose is to perceive the insensitive intentions perceived by the senses, and when desire for the object perceived by the senses becomes too strong, the estimative faculty is upset, and it feeds only on the phantom of the beloved person; then there is an inflammation of the whole soul and body, as sadness alternates with joy, because heat (which in moments of despair descends into the deepest parts of the body and chills the skin) in moments of joy rises to the surface, inflaming the face. The treatment suggested by Arnold consisted in trying to lose the assurance and the hope of reaching the beloved object, so that the thought would go away.
Why, in that case I am cured, or nearly cured, I said to myself, because I have little or no hope of seeing the object of my thoughts again, and if I saw it, no hope of gaining it, and if I gained it, none of possessing it again, and if I possessed it, of keeping it near me, because of both my monkish state and the duties imposed on me by my family's station. . . . I am saved, I said to myself, and I closed the book and collected myself, just as William entered the room.