XSLT 2.0 and XPath 2.0 Programmer's Reference, 4th Edition (371 page)
Read XSLT 2.0 and XPath 2.0 Programmer's Reference, 4th Edition Online
Authors: Michael Kay
Shortcut Semantics
XPath 1.0 defined that the right-hand operand of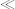 and
and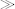 or
or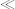 or
or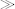 wasn't evaluated if the result could be established by evaluating the first operand (that is, if the first operand was false in the case of
wasn't evaluated if the result could be established by evaluating the first operand (that is, if the first operand was false in the case of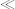 and
and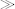 , or true in the case of
, or true in the case of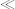 or
or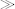 ). The reason for this rule was to give clearly defined behavior in the event of errors occurring. In XPath 2.0, the language designers have decided to sacrifice some of this predictability in favor of giving the implementation maximum freedom to rearrange expressions so that indexes can be used. For example, suppose you write an expression like this, to select all the male employees who are retiring today:
). The reason for this rule was to give clearly defined behavior in the event of errors occurring. In XPath 2.0, the language designers have decided to sacrifice some of this predictability in favor of giving the implementation maximum freedom to rearrange expressions so that indexes can be used. For example, suppose you write an expression like this, to select all the male employees who are retiring today:
//employee[@sex=‘M’ and @retirement-date=current-date()]
The XPath 1.0 rules say that you can't look at the retirement date until you've established that the employee is male. But if you have a hundred thousand employees, and they are indexed on their date of retirement, then the most efficient strategy would be to use the index, find the employees who are retiring today, and then select those among them who are male. The reason the rules were changed in XPath 2.0 is to allow systems to use this more efficient strategy.
Suppose you know that for female employees only (for some reason) the value of the
retirement-date
attribute might not be a date at all, but the string value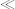 standard
standard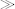 . A schema can be defined using a union type that allows the value to hold either a date, or this special value. The XPath 1.0 rules guaranteed that you would never look at the
. A schema can be defined using a union type that allows the value to hold either a date, or this special value. The XPath 1.0 rules guaranteed that you would never look at the
retirement-date
attribute of female employees while evaluating the expression, which would mean that you can never get the error that occurs when comparing the string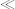 standard
standard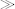 to a date. The XPath 2.0 rules don't give you this guarantee. To protect yourself against the failure, you could write:
to a date. The XPath 2.0 rules don't give you this guarantee. To protect yourself against the failure, you could write:
//employee[if (@sex=‘M’)
then @retirement-date = current-date()
else false()]
Unlike the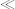 and
and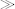 and
and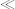 or
or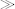 operators, the
operators, the if
if expression does give you a guarantee: if the condition is false, the
expression does give you a guarantee: if the condition is false, the then
then branch will not be executed. Similarly, if the condition is true, the
branch will not be executed. Similarly, if the condition is true, the else
else branch will not be executed.
branch will not be executed.