Breast Imaging: A Core Review (22 page)
Read Breast Imaging: A Core Review Online
Authors: Biren A. Shah,Sabala Mandava
Tags: #Medical, #Radiology; Radiotherapy & Nuclear Medicine, #Radiology & Nuclear Medicine
E. It will not affect the skin as breast cancer does, such as skin ulceration or dimpling.
61
Regarding male breast cancer, which one of the followings is correct?
A. It is not associated with Klinefelter syndrome.
B. The most common location is upper inner breast.
C. Most patients do not have BRCA gene mutations.
D. It is associated with gynecomastia.
E. Majority of the carcinoma is ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
62a
A patient is called back for additional views for a one-view finding on screening mammography in the central breast on the craniocaudal (CC) view. The asymmetry persists on spot compression views but is not seen on either the mediolateral oblique (MLO) or the true lateral projection, what is the next best step?
A. Perform ultrasound of the 12:00 and 6:00 positions, as well as the retroareolar plane.
B. Request the patient to return for a short interval follow-up in 6 months.
C. Recommend a breast MRI.
D. Perform rolled views.
62b
Rolled views were performed. On the CC rolled lateral (CC RL) view, the lesion moves laterally, this indicates that
A. The lesion is in the superior breast.
B. The lesion is in the inferior breast.
C. The lesion is in the central breast.
D. The lesion location cannot be determined based on the information provided.
63
A 72-year-old female presents with two new groups of suspicious calcifications in the right breast on screening mammogram. A two-site stereotactic core biopsy was performed. Pathology results of the core biopsy of both sites demonstrate atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH). What is the next best step for management of this patient?
A. Return to annual screening.
B. Recommend 6-month follow-up mammogram of the right breast.
C. Recommend surgical excision of both sites.
D. Recommend MRI to evaluate for underlying malignancy.
E. Recommend surgical excision of one site.
64
A 40-year-old female with a palpable lump presents for diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound for an abnormality seen on screening mammogram. Mammogram demonstrated a circumscribed oval mass (not shown). Ultrasound image is shown. The lesion was biopsied, and pathology results were pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH). Regarding PASH, which is the most accurate statement?
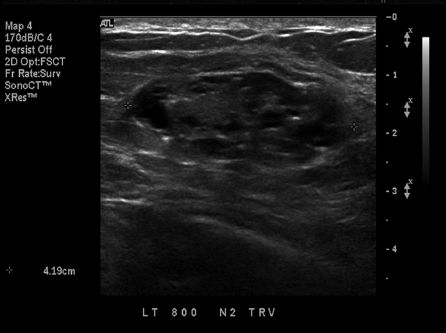
A. Usually presents as a spiculated mass.
B. Usually presents with calcifications.
C. Can present as a circumscribed mass but is often incidentally found on biopsy.
D. Is only an incidental finding and cannot present as a mass lesion.
65
An ultrasound was performed for a persistent focal asymmetry with associated pleomorphic calcifications. Based on the ultrasound image below, what is the next appropriate step in management?
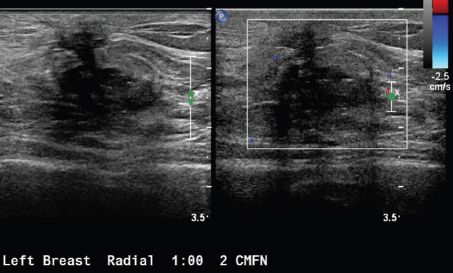
A. Ultrasound-guided core biopsy
B. Stereotactic core biopsy
C. MRI
D. 6-month follow-up
E. Annual diagnostic mammogram
66
A 60-year-old female presents for a diagnostic mammogram to workup calcifications in the lower inner quadrant of the left breast seen on recent screening mammogram. Skin calcifications are suspected. What is the most appropriate next step in determining the true nature of the calcifications?
A. Spot compression CC
B. True ML
C. Tangential view
D. Repeat MLO
67
Breast edema as the result of lymphatic obstruction and the presence of elongated, serpentine, nonductal calcifications on mammography most likely are due to:
A. Staphylococcus aureus infection
B. Streptococcus species infection
C. lymphoma
D. filariasis
E. congestive heart failure
68
A 65-year-old male with a strong family history of breast cancer presents for a diagnostic mammogram for palpable abnormalities in both breasts. Based on the images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
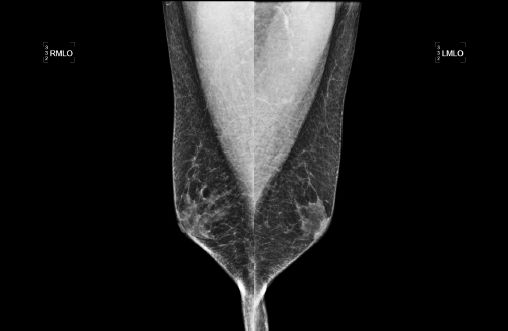
A. Gynecomastia
B. Fibrocystic change
C. Normal fibroglandular tissue
D. Breast cancer
69
A 50-year-old female presented for a screening mammogram, the MLO views of which are shown. What is the diagnosis?
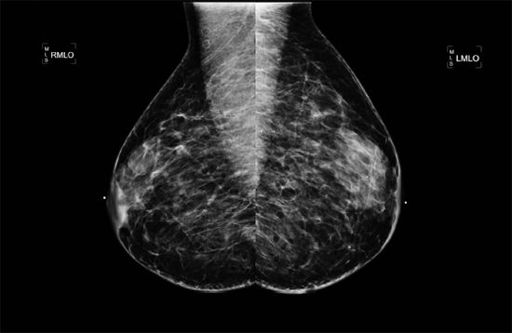
A. Neurofibromatosis
B. Steatocystoma multiplex
C. Malignancy
D. Silicone granulomas
70
Which of the following is correct about invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC)?
A. Higher false-negative rates are reported with ILC, than with any other forms of cancer.
B. ILC most commonly presents as calcifications.
C. MR imaging usually does not affect management of patients with ILC.
D. ILC has a lesser rate of multiplicity and bilaterality than invasive ductal carcinoma.
71
Which of the following statements is correct about inflammatory carcinoma of the breast?
A. It is considered a stage T1 lesion.
B. Most common presentation is skin erythema.
C. Majority of patients have axillary nodal involvement at presentation.
D. Inflammatory carcinoma accounts for 10% of breast cancers.
72
Regarding pregnancy-associated breast cancer, which of the following statements is correct?
A. It represents <1% of the breast cancers.
B. Breast cancer is the most common cancer during pregnancy.
C. At the time of diagnosis, pregnant women have larger and more advanced
cancers than nonpregnant women of the same age.
D. The average age of diagnosis is 40 to 45 years.
73
An MRI is shown from a patient with a palpable abnormality in the right breast. Based on these images, what is the most likely pathologic diagnosis?
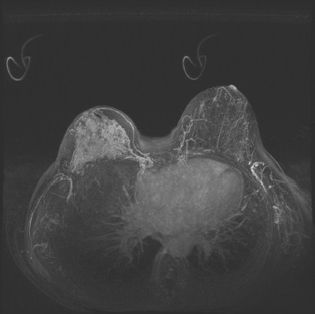
A. Invasive ductal carcinoma
B. Invasive lobular carcinoma
C. Fibroadenoma
D. Phyllodes tumor
74
In patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy, which is the best at assessing response to therapy?
A. Clinical exam
B. Mammography
C. Ultrasound
D. MRI
75
An MRI was performed in a patient with biopsy-proven breast cancer along the chest wall to evaluate for invasion of the pectoralis muscle. Which of the following criteria is most predictive of chest wall invasion?
Other books
Queen Bee Goes Home Again by Haywood Smith
Everything He Demands by Thalia Frost
Broken Bonds by Karen Harper
The Man Who Died by D. H. Lawrence
Against Our Will: Men, Women, and Rape by Susan Brownmiller
Angels and Ashes (Heaven's Rejects MC Book 2) by Avelyn Paige
The Wedding Gift by Lucy Kevin
(1993) The Stone Diaries by Carol Shields
Private Peaceful by Michael Morpurgo