Breast Imaging: A Core Review (26 page)
Read Breast Imaging: A Core Review Online
Authors: Biren A. Shah,Sabala Mandava
Tags: #Medical, #Radiology; Radiotherapy & Nuclear Medicine, #Radiology & Nuclear Medicine
109
If calcifications that are biopsied are calcium oxalate, how can they be identified by pathology?
A. Use hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining on the slides.
B. Do serial thin sections of the specimen.
C. Use polarized light on the slides.
D. Radiograph the paraffin block.
110
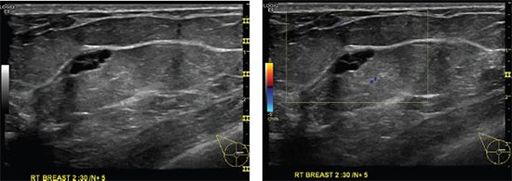
Which of the following statements about the mass depicted in the ultrasound images is correct?

A. Most common breast mass in women under the age of 35 years
B. Demonstrates rim enhancement on contrast-enhanced breast MRI
C. Benign tumor composed of mature adipose cells
D. Has a “breast-within-a-breast” appearance on mammogram
111
Which of the following statements is correct about the lesion depicted in the images below?
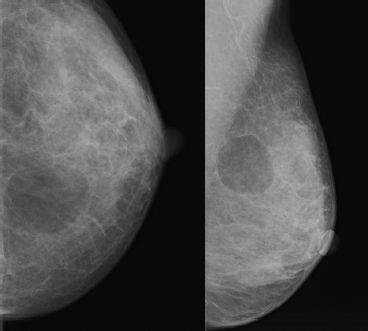
A. Fat and fibroglandular tissue are surrounded by a thin capsule or rim.
B. It never calcifies.
C. It is hard and immobile.
D. Mammography and ultrasound are usually needed to make the diagnosis.
112
A 62-year-old male presents with a palpable finding without history of trauma. What is the assessment and recommendation?
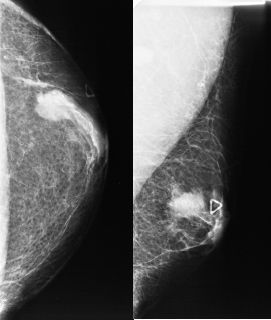
A. BI-RADS 2. Benign. No further follow-up needed.
B. BI-RADS 2. Benign. Referral to surgeon.
C. BI-RADS 3. Probably benign. Short-term follow-up in 6 months.
D. BI-RADS 4. Suspicious. Biopsy recommended.
113
Based on the images below, what is the assessment and next appropriate step in management?
A. BI-RADS 2. Benign. Return to annual screening mammography.
B. BI-RADS 3. Probably benign. Short-term follow-up in 6 months.
C. BI-RADS 4A. Low suspicion. Recommend biopsy.
D. BI-RADS 4C Moderate suspicion. Recommend biopsy and scan the ipsilateral axilla.
114
Match the lymph nodes draining the breast to their location.
| 1. Level I nodes | A. Behind the pectoralis minor muscle |
| 2. Level II nodes | B. Infralateral to lateral edge of the pectoralis muscle |
| 3. Level III nodes | C. Medial to pectoralis muscle |
| D. Between pectoralis minor and subclavius muscle |
115
Images below represent a mass in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. This was biopsied. Pathology results are malignant phyllodes.
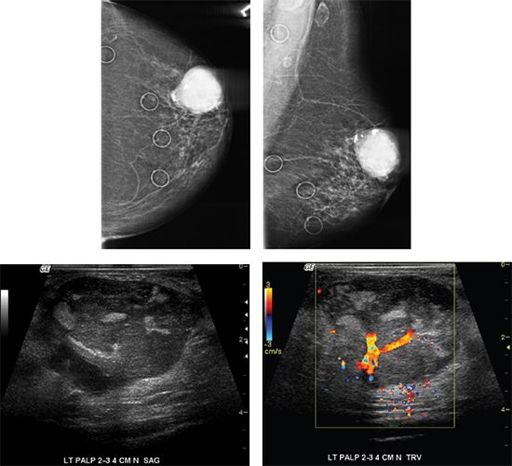
Which of the following statements concerning malignant phyllodes tumor is correct?
A. About half of all phyllodes tumors are malignant.
B. Most common sites for metastases are axillary lymph nodes.
C. There are no hereditary factors associated with these tumors.
D. Treatment of choice is neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
116
Which of the following statements concerning invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is correct?
A. Grows as single-file linear columns of tumor cells with intervening stroma.
B. It comprises sixty to seventy percent of all invasive breast cancers.
C. Microscopically, proliferating epithelium is present in villous-like projections.
D. Slow growing with as 95% to 98% 5-year survival.
117
Which of the following statements about the lesion seen on the MRI is correct?

A. Most commonly seen in young women
B. Occurs as a result of hormone replacement therapy
C. Uniformly echogenic on ultrasound
D. Most commonly seen in the upper outer quadrant
118
Which of the following can be a cause for the finding below?
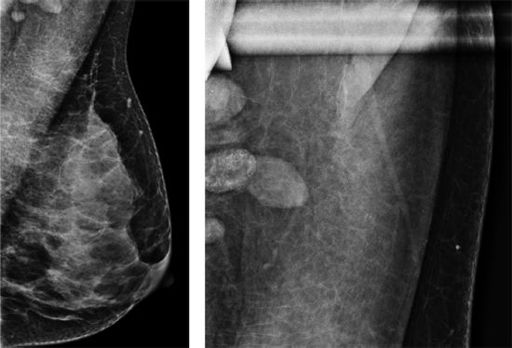
A. Implant rupture
B. Lymphoma
C. PASH
D. Mastitis
119
Based on the images from screening mammogram below, what is the appropriate BI-RADS category? The patient has known lymphoma.

A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 1
C. BI-RADS 2
D. BI-RADS 3
E. BI-RADS 4
120
A 43-year-old female presents with new right breast nipple retraction. What is the appropriate next step in the patient’s management?
A. Galactography of the retracted nipple
Other books
Fool Errant by Patricia Wentworth
Abiding Peace by Susan Page Davis
Bluebonnet Belle by Lori Copeland
Where the West Wind Blows by Mary Middleton
The Crimson Campaign by Brian McClellan
The Postcard by Tony Abbott
The Worst Witch Strikes Again by Jill Murphy
Black Butterfly by Michelle, Nika
The Big Fix by Brett Forrest
Wishes on the Wind by Elaine Barbieri