i bc27f85be50b71b1 (185 page)
Read i bc27f85be50b71b1 Online
Authors: Unknown
Incontinent Urinary Diversion
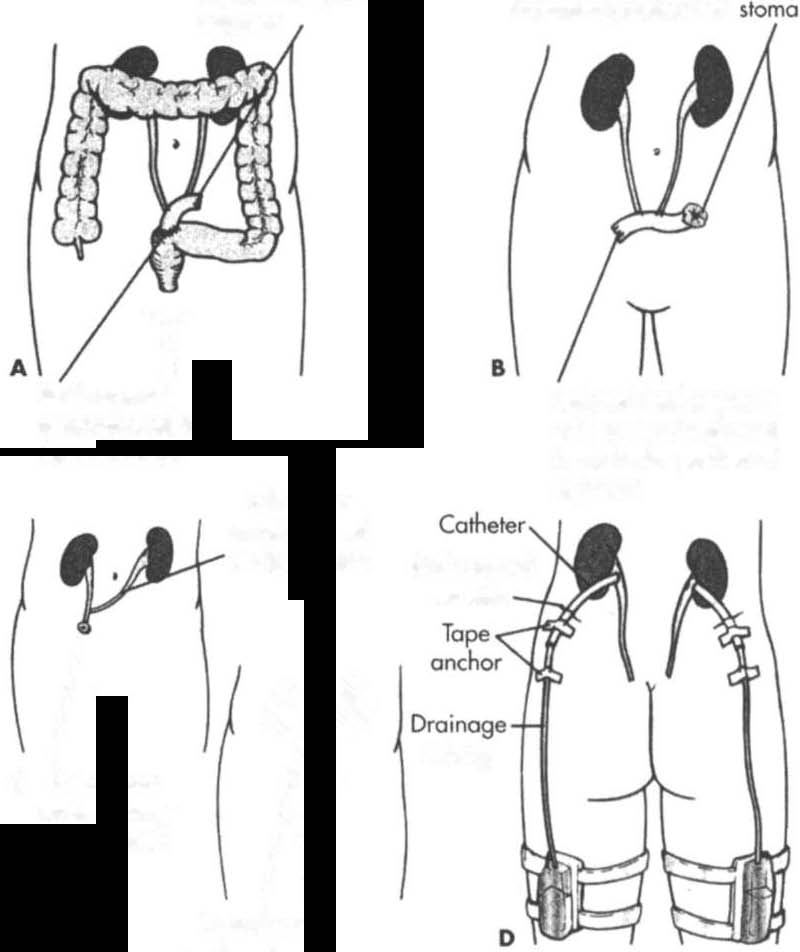
Incontinent urinary diversion involves diverting urine flow to the skin
through a stoma, which rhen requires an external appliance to collect
urine. Segments of the ileum or colon are generally used as a conduit
to bridge the gap from the ureter to the skin when the bladder must
be removed or bypassed (see Figure 9-7). Once the diversion is complete, urine drains from the Stoma into the collecting device every few seconds. These segments of intestine become totally isolated from the
gastrointestinal rracr.3.47 Bladder carcinoma and severe neuropathic
bladder dysfunction are common indications for this procedure.
Continent Urinary Diversion
COlltillent urinary diversions are internal urine reservoirs that are surgically constructed from segments of the ileum, ileocecal segment, or colon. The internal reservoirs eliminate the need for external appli-

598 AClITE CARE HANDBOOK FOR I'HYSICAL THERAPISTS
Isolated ileal segment
with ureters implanted
in posterior portion of
segment
Protruding abdominal
IT
Ileal segment
Isolated ileal segment
anastomosed to
with ureters implanted
sigmoid colon
in posterior portion of
�menl
Left ureter
anostomosed
to right ureter
Stab woond
on skin
/11
tubing
Cutaneous
�,�
C
ureterostomy
on abdomen
ti
Cutaneous
ureterostomy
Posterior view
on abdomen
Bilateral nephrostomy tubes
inserted into renal pelvis;
catheters exit through an
incision on each Rank, or
there may be just one
kidney
Figure 9-7. Methods of urinary diversion. A. Ureteroileosigmoidostomy.
B. lIeal loop (or ileal conduit). C. Ureterostomy (transcutaneous lIreteros·
tomy and bilateral cutaneous ureterostomies). D. Nephrostomy. (With permission from SM Lewis, MM Heitkemper. SR Dirsksen leds). Medical
Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management ofClin;cal Problems 15th ed/.
St. LOII;s: Mosby, 2000; 1292.)

GENITOURINARY SYSTEM
599
ances and allow more control for the patient. The internal reservoir is
connected to an abdominal stoma, which does nOt continually drain
urine, and patients perform intermittent self-catheterizations through
the Stoma (see Figure 9_7).42.47
Orthotopic Bladder Substitution
Orthotopic bladder substitution involves reshaping a portion of the distal ileum into a neobladder and connecting the ureters and the urethra to it. Connecting the urethra to the neobladder allows for natural micturition. However, incontinence still may occur occasionaiJy with this procedure, and the patient may also require intermittent catheterization.47
Physical Therapy IIztervention
The following are general goals and guidelines for the physical therapist when working with patients who have genitourinary dysfunction.
These guidelines should be adapted to a patient's specific needs.
The primary physical therapy goals in this patient population are similar to those of other patients in the acute care setting. These goals are to (1) optimize safe functional mobility, (2) maximize activity tolerance and
endurance, and (3) prevent postoperative pulmonaty compLications.
General physical therapy management guidelines and considerations revolve around the normal functions of the genitourinary system that are disrupted by the various disorders discussed earlier in this chapter. These include, but are nOt limited to, the following:
1.
Evaluating laboratory values before examination or inter-
vention can help the physical therapist decide which particular
signs and symptoms to monitor as well as determine rhe parameters of the session. Refer to Appendix LI for more information on fluid and electrolyte imbalance.
2.
The inability to regulate cellular waste products, blood
volume, and electrolyte levels can result in:
•
Mental status changes fcom a buildup of ammonia, BUN,
Cr, or a combination of these. If this situation occurs, then
the therapist may choose to modify or defer physical therapy
intervention, particularly educational activities that require
concentration.
•
Disruption of excitable tissues such as peripheral nerves
and skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle from altered levels
of electrolytes.53 If this situation occurs, then the therapist

600 AClITE CARE HANDBOOK FOR PHYSICAL ll-iERAPISTS
may need to reduce exercise intensity during muscle strengthening activities. Additionally, if peripheral neuropathy results in sensory deficits, then the therapist needs to take the appropriate precautions with the use of modalities and educate the patient on protective mechanisms to avoid skin breakdown.
•
Peripheral or pulmonary edema from inability to excrete
excess body fluids.53 Pulmonary edema can re ult in shortness of
breath with activities and recumbent positioning. Peripheral
edema can result in range-of-motion limitations and skin breakdown. Refer ro Table 1-6 for a description of pitting edema, and see Chapter 2 for a description of pulmonary edema.
3.
Blood pressure regulation can be altered by the inability to
excrete body fluids and activate the renin-angiotensin system.53
4.
Activity rolerance can be reduced by the factors mentioned
in this list, as well as anemia that can result from decreased erythropoietin secretion from kidneys, which is necessary for stimulating red blood cell production.53
5.
Patients with CRF may present with concurrent clinical
manifestations of diabetes mellitus, as diabetes mellitus is a strong
contributing factor to this disorder. Refer to Chapter I I for more
information on diabetes mellitus.
6.
As stated in the introduction ro this chapter, patients with
genirourinary dysfunction may have referred pain (see Table 9-1).
Physical therapists can play a role in differentiating the source of a
patient's back pain as well as providing symptomatic management
of this referred pain.
7.
Patients who are status post surgical procedures with
abdominal incisions are less likely to perform deep breathing and
coughing because of incisional pain. Diligent position changes,
instruction on incisional splinting during deep breathing, and
coughing, along with early mobilization, help prevent the development of pulmonary complications.
S.
For patients who are ambularory and present with urinary
urgency, possibly from diuretic therapy, the use of a bedside commode may be a beneficial recommendation to minimize the incidences of incontinence.
9.
Patients who are incontinent may benefit from a home exer-
cise program, referral ro a physical therapist who specializes in pelvic floor strengthening, or both on discharge from the hospital.

