i bc27f85be50b71b1 (66 page)
Read i bc27f85be50b71b1 Online
Authors: Unknown
Segmental instabil
Fusion of the facet joints
ity, fractures,
using hardware and bone
facet joint arthrigraft. May use fusion cages
tis
or pedicle screws and rods
to achieve fixation.
Approaches can vary, and
a fusion can be done in
conjunction with other spinal procedures to decompress nerve roots.
"'These procedures may be performed in any area of [he spine when indicated. The
approach may be anterior, posterior, or posterolateral.
Sources: Adapted from GW Wood. Lower Back Pain and Disorders of lntervenehral
Disc. In ST Canale (cd), Campbell's Opcrarive Onhopacdics, Vol. 1 (9th ed). St. Louis:
Mosby, 1998; and JJ Regan. Endoscopic Spinal Surgery Anterior Approaches. In jW
Frymoyer (cd), The Adult Spine Principles and Pracrice (2nd cd). New York: Lippincott-Raven, 1997.

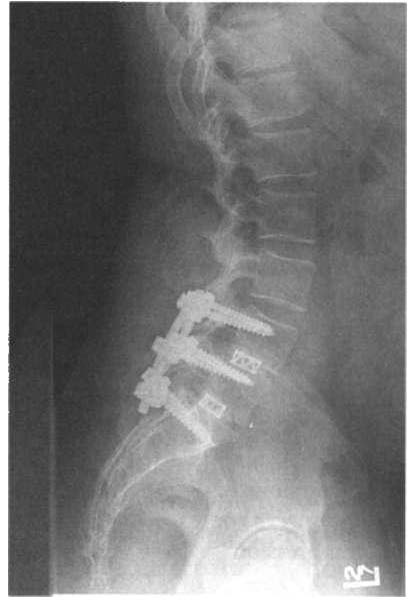

212 AClJrE CARE HANDBOOK FOR I'HYSICAL THERAPISTS
Figure 3-20. Lateral view o( a posterior interbody (usion with pedicle screws.
Pain that arises from spinal instability caused by degenerative disc
disease or degenerative joint disease may be treated surgically with a
spinal fusion. Anterior or posterolateral spinal fusion with decompression attemptS to fuse unstable spinal segments. This is achieved through implantation of various types of instrumentation with bone
grafting to create a single motion segment and eliminate the source of
pain, the disc.58 The spinal segments are fixed using different types of
rods, plates, and pedicle screws. The usc of interbody fusion cages
with instrumentation has become common practice for spinal fusion.
An anterior lumbar interbody fusion, posterior lumbar interbody
fusion (Figure 3-20), or combination can be performed 56 Titanium
alloy fusion cages are placed within the vertebral spaces, replacing the
degenerated disc. These cages are then packed with bone graft harvested from the iliac creSt (autograft) or from a bone bank (allograft).
This bone graft can be supplemented with osteoinductive growth fac[Qrs to facilitate fusion.59 A combination of an anterior and posterior fusion can be successful when a single approach fails.
Experimental designs of the total disc replacement have been developed to reconstruct the disc, maintain disc height, and preserve seg-


MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
213
mental motion of the spine .60 Developers of the artificial disc
replacement believe that restoring mobility will decrease degeneration
of spinal segments above and below the affected segment." Artificial
disc implantation has been occurring in Europe, and clinical trials arc
beginning in the United States. Many generations of the total disc
design have shown promise, and if clinical trials are favorable, the
total disc replacement may become a tool to combat back pain.61
Complications that can occur postoperatively from spinal surgery
are neurologic injury, infection, cauda equina syndrome, dural tear
with cerebrospinal fluid leak, and nonunion, as well as general surgical complications noted in previous seccions.
Physical Therapy IlIleroelltioll after Spillal Surgery
In the acute care setting, physical therapy should emphasize early
functional mobilization, education on proper body mechanics, gait
training, and assessment of assistive devices to increase patient safety.
Patients should be educated on movement precautions to minimize
bending and twisting with activity, lifting restrictions per the surgeon,
and use of braces or corsets if prescribed .
•
Patients should be taughr to logroll to get out of bed. The body
rolls as a unit, minimizing trunk rotation. Functional mobility
training should begin the first postoperative day. Ambulation
should be stressed as the only formal exercise postoperatively for
spinal surgery to promote healing of all tissues.
• Symptoms, such as radiating pain and sensory changes present
before surgery, may persist for a significant period postoperatively
secondary to edema surrounding the surgical site. Patients should
be educated to this fact and told if any significant increase in pain
or change in bladder and bowel function occurs, the patient should
notify the nurse, surgeon, or both, immediately.
Clinical Tip
• For surgical procedures with an anterior approach, the
patient should be given a splinting pillow and educated in
its use to promote deep breathing and coughing. A corset
can be use to aid patient comfort with activity.

214
ACtITE CARE HANDBOOK FOR PHYSICAL THERAPISTS
o Rolling walkers are useful to promote a step-through
gait pattern and decrease stress on the spine caused by lifting a standard walket. Patients should progress to a cane or no assistive device to promote upright posture.
o
If an iliac crest bone graft is harvested through a second
incision, a patient may complain of increased pain at the
surgical site. Ice can decrease swelling at the donor site.
With this rype of graft, a patient wiiJ likely need an assistive
device to increase safery with ambulation and decrease pain.
o
If interbody fusion cages are used, the patient should be
encouraged to sit in a chair as soon as possible to increase
compression on the cage and promote bone ingrowth. Sitting time can be unlimited according to patient comfort.56
o Patients who have undergone spinal fusion should be
educated about the adverse effect that cigarette smoking
has on the success of fusion.·' The health-care team
should emphasize smoking cessation, or the patient should
be given the appropriate resources to assist with this task.
o The physical therapist should always check orders for
braces used by the surgeon and any other restrictions on
activity. Braces are usually worn when the patient is out of
bed. If necessary, a surgeon may limit raising the head of the
bed. Reverse Trendelenburg (putting the whole bed at a 45-
degree angle, with head up) can assist with patient ADLs.
o Treatment should be coordinated with the administration of pain medication. Patients should be educated in
relaxation techniques or breathing exercises to help manage their pain. The physical therapist should also be aware
of any psychosocial factors that can interfere with patient
recovery. If necessary, consult the psychiatric or chaplain
services to assist with a patient'S coping skills.
Soft Tissue Surgeries
There is a wide variety of soft tissue surgeries encountered in the
acute care orthopedic setting. The majoriry of these surgeries are
aimed at improving joint stability by repairing the functional length
of muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Common soft tissue surgeries
include tendon transfers, muscle repairs, fasciotomies, cartilage resec-
