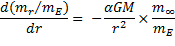Judgement Day (17 page)
Authors: Michael Spears
Tags: #apocalypse, #messiah, #armageddon, #last days, #judgment day, #judgement day
(6)
It must be kept in
mind that energy is always conserved, that energy remains constant
no matter what the change in the sot, according to this theory
energy only ever appears to change due to changes in the
measurement of time.
Now we must consider
the equation for kinetic energy
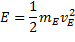
(7)
(Where v
E
=
velocity from the perspective of an observer on earth.)
According to the above
hypothesis, if mass decreases in weaker gravitational fields (for
example) velocity squared must increase proportionally. Now we can
understand mathematically the reason why when time is faster
everything moves more easily through space. In weaker gravitational
fields not only does light move faster, but so too do objects of
mass. Objects of mass must move faster in weaker gravitational
fields because their mass decreases while their kinetic energy
remains constant thus resulting in an increased velocity, from the
perspective of someone on earth of course.
The next equation to
consider is the simplified equation for gravitational potential
energy
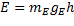
(8)
(Where g
E
=
gravitational acceleration from the perspective of an observer on
earth.)
According to this
equation, if mass ‘m
E
’ decreases then gravitational
acceleration ‘g
E
’ must increase proportionally. Now
let’s consider the proper equation for gravitational acceleration,
recall that if mass decreases the sot increases and gravitational
acceleration increases
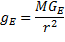
(9)
(Where G
E
=
the universal gravitation constant from the perspective of an
observer on earth, r = the distance from the centre of mass (or the
radius), M = the mass of the object creating the gravity in
question.)
Now we must conclude
that if the mass of an object subject to gravitational acceleration
decreases the value for the gravitational constant ‘G
E
’
must increase proportionally. Consider next the S.I. units
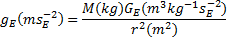
We can see that the
value for the gravitational constant changes depending on the
strength of the gravitational field an object subject to gravity is
in, or if you prefer, the value of the gravitational coefficient
changes depending on the sot in that location in space. I propose
changing the name of the gravitational constant to the
‘gravitational coefficient’.
Let’s stop for a
moment and think about the equations we have been discussing and
their full implications. I have now developed a series of equations
from the reinterpretation of one single experiment. What we’ve
learned is that mass decreases in weaker gravitational fields, the
combination of this decrease in mass and the conservation of energy
results in an increase in the velocity of matter and energy, and an
increase in the gravitational acceleration of matter. What we’ve
learned is that in weaker gravitational fields, when time is
faster, everything moves faster. While it may seem
counter-intuitive that light would accelerate due to gravity,
rather than decelerate, it is important to recall another of
Einstein’s equations
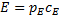
(10)
(Where p
E
=
momentum from the perspective of an observer on earth.)
According to this
equation, if gravitational field strength decreases, time becomes
faster and light accelerates, then the momentum of light must
decrease proportionally to any increase in the speed of light. So
while light may not slow due to gravity, and it is actually the
opposite that occurs, gravity affects the momentum of light. It
makes sense now that since gravity changes the momentum of light
that the path of light can be bent by gravity, as predicted by
Einstein.
Consider now what the
implications of assuming light speed to be constant might be, for
example, we use electromagnetic radiation (emr) to measure
distances within the solar system. If this hypothesis is correct
our measurements of the solar system must be very slightly
incorrect, as emr moves away from the sun time must become faster,
emr must accelerate, and the outer planets must be further away and
moving faster than what is presently believed. If this hypothesis
is correct, the size of the solar system could be an optical
illusion. Of course, were you to send a spacecraft to a planet on
the outskirts of the solar system as time becomes faster that
spacecraft would also accelerate, just the same way that light
would. We could never know that our measurements are an illusion
unless we could observe gravitational motion in its entirety, from
outside a gravitational field, not from within it. The true extent
of this effect within our solar system is difficult to calculate,
for reasons which will become clearer shortly, but I am certain
that it can be calculated.
Think now about stars
on the outskirts of galaxies, stars on the outskirts of galaxies
have been found to be moving faster than predicted by the theories
of Newton and Einstein, the most popular explanation for observed
galactic rotation curves is that there must be a large amount of
unseen matter in galaxies, it is known as the theoretical dark
matter. However if my theory is correct it may be that dark matter
is unnecessary and that galaxy rotation curves can be explained by
a new understanding of exactly how gravity works.
Part 1c: Gravitational
Time Dilation and Dark Matter
According to my theory
mass varies as a function of gravitational field strength which
creates a change in time due to conservation of kinetic energy and
gravitational potential energy.
The scalar equation
for gravitational field strength is
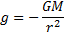
Now we wish to
consider changes in the mass of an object in a particular
gravitational field ‘m
r
’ with respect to mass as
experienced on Earth ‘m
E
’. We also need to consider that
mass will reach a minimum at a theoretical infinite distance from
the gravitational field it is a part of. However it becomes
difficult because everything is a part of a different gravitational
field. Although the speed of time on Earth would be equal to 1,
Earth is primarily a part of the gravitational field of the Sun, so
at a theoretical infinite distance from the Earth
m
∞
/m
E
< 1 or t
∞
/t
E
< 1 or Δt
∞
/Δt
E
> 1 and is dependent on
the gravitational field strength of the Sun. The Sun in turn is
primarily a part of the gravitational field of the Milky Way, and
the Milky Way a part of the local universe around it.
When discussing
changes in time it is important to remember that when time is
faster a second becomes shorter,
so the “length” or “size” of an earth second decreases.
This means that more seconds pass relative to an earth second,
thus
it is easier to think in terms of changes in time, how
much time has passed for an object in comparison to how much time
has passed on earth
.
T
his way when time is
faster the ratio Δt
r
/Δt
E
is greater and vice
versa when time is slower
, this
ratio is the inverse of
t
∞
/t
E
.
To determine the
change in the mass of an object as a function of distance from the
centre of mass of an object we can thus write the equation