Pediatric Primary Care (101 page)
E. Physical findings.
1. Ketonuria, ketonemia, glucosuria.
2. Vomiting.
3. Dehydration.
4. Slow, labored breathing, flushed face and cheeks.
5. Mental confusion, lethargy.
6. Fruity odor to breath.
7. High blood glucose levels.
8. Monilial vaginitis in adolescent females.
F. Diagnostic tests.
1. Fasting plasma glucose, casual plasma glucose.
2. Urine for ketones and glucose.
3. Electrolytes and pH.
4. Blood urea nitrogen.
5. CBC.
G. Differential diagnosis.
| Hypoglycemia, 251.2 | Salicylate intoxication, 535.4 |
| Intracranial lesions, 784.2 | Sepsis, 038.9 |
1. Hypoglycemia.
2. Salicylate intoxication.
3. Sepsis.
4. Intracranial lesions.
H. Treatment.
1. Multidisciplinary approach involving family with pediatric endocrinologist, PNP, diabetic nurse educator, social worker, nutritionist.
2. Educate child and family in stabilizing blood sugars, diabetes management. Due to complexity of illness, management requires incorporation into daily life.
3. Treatment replaces insulin that child is unable to produce—the cornerstone of management.
4. Insulin dosage is tailored to child's blood glucose and HbA1c levels
Table 29-1
.
Diabetic control: based on HbA1c levels, clinical symptoms. HbA1c levels provide information on glycemic control during past 60 days.
5. Insulin is categorized by peak of onset.
6. Various insulin injection devices available.
Table 29-1
HbAlc and Glycemic Targets
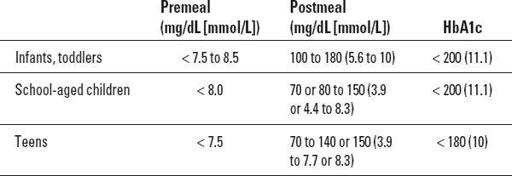
Source:
Kaufman, F. (2003). Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Pediatrics in Review, 24
, 9.
I. Follow up.
1. Review medical, nutritional, insulin therapy, daily blood glucose monitoring
(Table 29-2
).
2. Follow up every 3 months to review management plans, physical/ psychosocial needs
(Table 29-3
).
J. Complications.
| Eating disorders, 307.5 | Neuropathy, 357.2 |
| Ketoacidosis, 250.1 | Retinopathy, 362.1 |
| Nephropathy, 583.9 | Vaginal yeast infections, 112.9 |
1. Ketoacidosis.
2. Vaginal yeast infections.
3. Retinopathy.
4. Nephropathy.
5. Neuropathy.
6. Lipid profile.
7. Eating disorders.
K. Education.
1. Prevention of diabetic ketoacidosis.
2. Knowledge of onsets of action, peak action, duration of action of five types of insulin
(Table 29-4
).
3. Recognition of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
4. Management of hypoglycemia: evening protein or fat snack to prevent hypoglycemia.
Table 29-2
Principal Adjustments in Basic or Set Insulin Dose
| Rapid-, short-, intermediate-, or long-acting insulin is adjusted after a pattern has been identifi ed over 3-7 days. | |
| Increase or decrease by 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, or 2.0 units (10% of dose). | |
| Time of test | Change this insulin |
| 2 or 3 insulin injection | |
| Before breakfast | Evening intermediate- or long-acting |
| Before lunch | Morning rapid- or short-acting |
| Before dinner | Morning intermediate- or long-acting |
| Before bedtime | Evening rapid- or short-acting |
| In the night | Evening intermediate- or long-acting |
| Multiple insulin injections Same as above except: | |
| Before dinner | Lunch rapid- or short-acting |
| Insulin pump | |
| Change bolus dose if blood glucose abnormal | < 2–3 hours after the meal |
| Change basal dose if blood glucose abnormal | > 3 hours after the meal |
| Recheck to be sure the changes made return blood glucose levels to the target range. |
Source:
Kaufman, F. (2003). Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Pediatrics in Review, 24
, 9.
5. Prevention of long-term complications.
6. Role of exercise in management: Exercise improves glucose utilization.
7. Insulin therapy and monitoring of glucose levels.
8. Meal planning, nutrition: Eat meals and snacks within 1 hour of usual time.
9. School issues and coping skills.
10. Monitoring weight: Maintain ideal body weight.
Table 29-3
The Outpatient Visit for Patients with Diabetes
| Physical examination | Frequency recommendations |
| Weight, height, body mass index (BMI) | Every 3 months/assess changes in percentile |
| Sexual maturity rating stage | Every 3 months/note pubertal progression |
| Blood pressure | Every 3 months/target < 90th percentile for age |
| Eye | Dilated funduscopic examination every 12 months after 5 years of diabetes |
| Thyroid | Every 3 months/presence of goiter, signs of thyroid dysfunction |
| Abdomen | Every 3 months/presence of hepatomegaly, fullness, signs of malabsorption, inflammation |
| Foot, peripheral pulses | Every 3 months inspection/after 12 years of age, thorough |
| Skin, joints, injection sites | Every 3 months/injection sites, joint mobility, lesions associated with diabetes |
| Neurologic | Every 12 months/signs of autonomic changes, pain, neuropathy |
| Laboratory test | Frequency |
| HbA1c | Every 3 months |
| Microalbuminuria | Every 12 months after puberty or after 5 years of diabetes |
| Urinalysis, creatinine | At presentation and with signs of renal problems |
| Fasting lipid profile | After stabilization at diagnosis and every few years |
| Thyroid function tests, including antithyroid antibodies | Every 12 months |
| Celiac screen | At time of diagnosis; if symptoms, at puberty |
| Islet antibodies | At diagnosis |
Source:
Kaufman, F. (2003). Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Pediatrics in Review, 24
, 9.
Table 29-4
Onset of Action, Peak Action, and Duration of Action in Five Types of Insulin
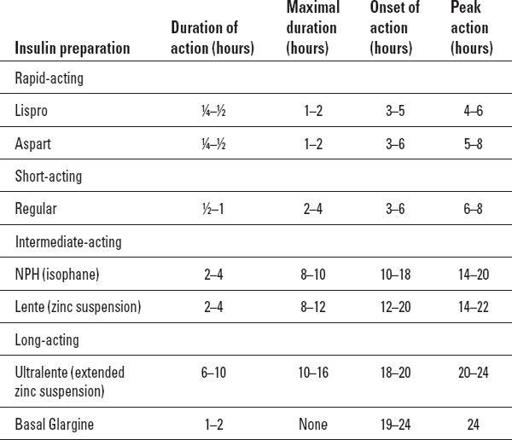
Source:
Kaufman, F. (2003). Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Pediatrics in Review, 24
, 9.
V. TYPE 2 DIABETES
| Acanthosis nigricans, 701.2 | Polydipsia, 783.5 |
| Dyslipidemia, 272.5 | Polyuria, 788.42 |
| Dysuria, 788.1 | Sleep apnea, 780.57 |
| Family history of type 2 diabetes, V18 | Type 2 diabetes, 250 |
| Hypertension, 401.9 | Vaginal infection, 616.1 |
| Obesity, 278 | Weight loss, 783.2 |
A. Chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance.
B. Etiology.
1. Most common clinical factor for type 2 diabetes is obesity/body mass index (BMI) > 85% for age and sex.
C. Occurrence.
1. Female-to-male ratio is 1.7:1 regardless of race. Youths between 8-19 years of age.
D. Clinical findings.
1. Obesity.
2. Polyuria.
3. Polydipsia and weight loss.
4. Vaginal infection as chief complaint.
5. Dysuria.
6. Family history.
Other books
But What If We're Wrong? by Chuck Klosterman
Lor Mandela - Destruction from Twins by L Carroll
The Revenge of Captain Paine by Andrew Pepper
Broadway's Most Wanted by Tom Shea
Framingham Legends & Lore by James L. Parr
Atticus Claw Goes Ashore by Jennifer Gray
Beautiful Death (Bella Morté Trilogy Book 1) by Walker, L. Dee
The Matzo Ball Heiress by Laurie Gwen Shapiro
Cole's Christmas Wish by Tracy Madison
The Blood King by Brookes, Calle J., Lashbrooks, BG