Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed (228 page)
Read Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed Online
Authors: Noel Morimoto
server or servers. As recommended previously, pre-create the file share on an NTFS folder
and properly configure the share and NTFS permissions for each folder target that will be
added to the folder.
When a new folder is created with multiple folder targets, a replication group can be
created at the same time. To create a folder within an existing namespace, perform the
following steps:
1. Log on to the Windows Server 2008 R2 system with an account with local server
administrator privileges.
Installing DFS
1159
2. Pre-create and set NTFS permissions on the servers and shares that will host the DFS
namespace folder.
3. Click Start, click All Programs, click Administrative Tools, and select DFS
Management.
4. Select the Namespaces node, and then double-click the Namespaces node to expose
the existing namespaces.
5. If the desired namespace does not appear, in the Actions pane, click on the Add
Namespaces to Display link and follow the steps to search for and add an existing
namespace to the console view.
6. Select the desired existing namespace, and in the Actions pane, click on the New
Folder link.
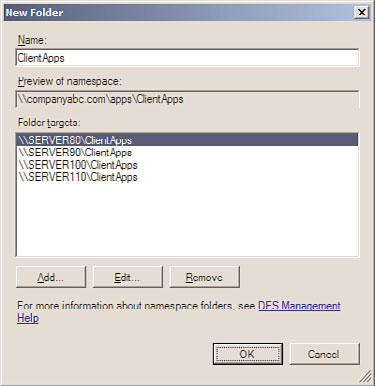
7. When the New Folder window opens, type in the name of the folder and click the
Add button to locate the folder targets.
8. After all the folder target servers have been added to the New Folder window, click
OK to continue, as shown in Figure 28.24.
ptg
28
FIGURE 28.24
Defining a new folder and folder targets.
9. When a new folder is created and multiple targets are specified, a Replication pop-up
window opens, asking if a replication group should be created. Click Yes to create a
new replication group for the folder targets.
10. When the Replication Group and Replicate Folder Name window opens, review the
name of the proposed replication group name and the replicated folder name, and
click Next to continue. The prepopulated names will match the namespace and
folder names.
11. The Replication Eligibility page will display whether or not each of the folder targets
are capable of DFS Replication. If all targets are eligible, click Next to continue.
1160
CHAPTER 28
File System Management and Fault Tolerance
12. On the Primary Member page, click the Primary Member drop-down list arrow and
select the folder target server that will be used to populate the remaining member
folder targets. The data that exists in the folder of the primary target member will be
replicated to each of the other targets. After selecting the desired primary server,
click Next to continue.
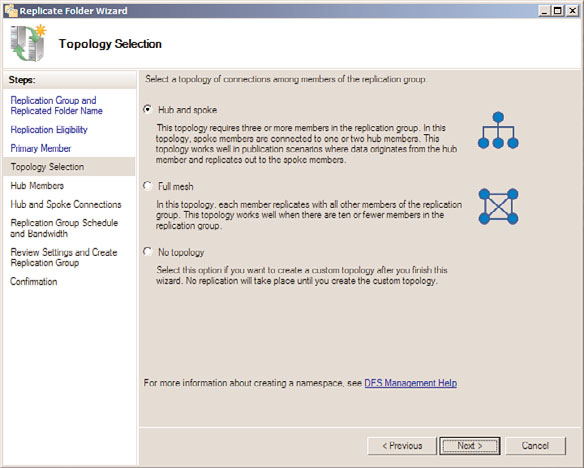
13. On the Topology Selection page, select the desired replication topology. For this
example, select the Hub and Spoke option button, as shown in Figure 28.25, and
click Next to continue.
ptg
FIGURE 28.25
Selecting the hub and spoke replication topology.
14. On the Hub Members page, all servers will initially be listed in the Spoke Member
section. Double-click the desired servers to move them to the Hub Member section,
if they will be used as a hub server. Hub servers will replicate with all other servers
and spoke servers will only replicate with the hub servers defined on this page. Once
all the necessary hub servers are in the Hub Member section, click Next to continue.
15. On the Hub and Spoke Connections page, each of the spoke servers will be listed
with their required hub member and an optional hub member. Optional hub
members will only be populated if multiple servers are selected as hub members in
the previous step. Even though the hub servers are listed as required and optional,
the spoke servers will replicate with both and a connection between each hub
Installing DFS
1161
server and spoke system will be created. Also, hub servers will replicate with one
another as well.
16. On the Replication Group Schedule and Bandwidth page, select the desired band-
width limitation if desired or set the hours replication to allowed, and click Next
to continue.
17. On the Review Settings and Create Replication Group page, review the selections
and if everything looks correct, click Create.
18. On the Confirmation page, if the replication group creation tasks were all completed
successfully, click Close. Otherwise, select the Errors tab and review and repair the
errors, and rerun the Replication Group Creation Wizard.
19. Once the window is closed, back in the DFS Management console, double-click on
the Replication node to reveal the new replication group and select it.
20. In the tasks pane, with the new replication group selected in the tree pane, select the
Connections tab to review the connections created from the previous steps.
Best Practices for DFS Replication
Following best practices for DFS Replication can help ensure that replication occurs as
expected. Because file replication is triggered by a file version change or last-saved or
ptg
modified time stamp, a standard file share might generate many replication changes,
which can saturate the network bandwidth if no bandwidth constraints are placed within
DFS Replication connections. To avoid such scenarios, follow as many of these suggestions
as possible:
. Start with empty DFS namespace folders and targets to keep from having to replicate
any data at the root level. Also, this can simplify the restore process of a DFS root
folder because it contains only folders that are managed by DFS.
. Do not replicate data between DFS namespace shares because the namespace shares
28
will try to replicate the data in the namespace folders as well as the data contained
within the folder targets. Replication is not necessary if the folder targets are already
replicating. Because the roots will not replicate for redundancy, deploy domain DFS
namespaces and add additional namespace servers.
. Back up at least one DFS folder target and configure the backup to not update the
archive bit. Changing the archive bit might trigger unnecessary replication.
. Thoroughly test server operating system antivirus programs to ensure that no adverse
effects are caused by the scanning of files on a replicated DFS target. Also, configure
server antivirus to scan at write operations only and configure clients to scan on read
operations to ensure complete antivirus protection for DFS servers and clients.
. Verify that the drive that will contain the staging folder for a replication connection
contains ample space to accept the amount of replicated data sent and received by
the server.
1162
CHAPTER 28
File System Management and Fault Tolerance
Having a high number of read-write operations is not desirable because it causes heavy
replication, and in a scenario like this, DFS Replication should be performed during off-
peak hours unless Windows Server 2008 R2 DFS Replication can be used in conjunction
with bandwidth constraints.
Configuring DFS Read-Only Replication
Windows Server 2008 R2 now allows for a replicated folder to be defined as read-only. This
can be configured once a replication group is defined. As a best practice, when read-only
replicated folders are desired, select the No Topology option button on the Topology
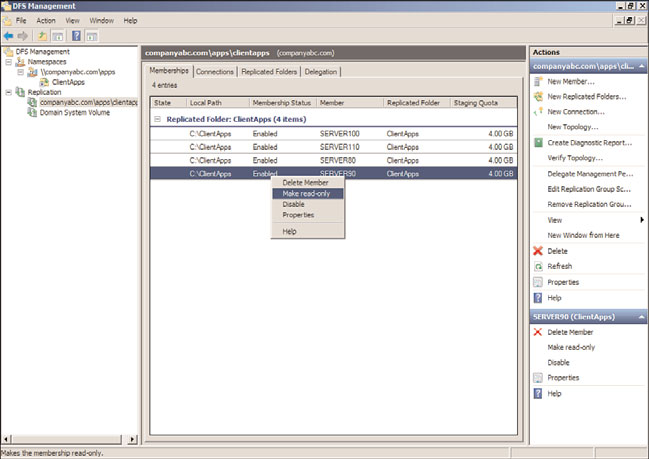
Selection page when running the Replicate Folder Wizard. Once a replication group is
created, select the replication group in the tree pane, and in the tasks pane select the
Memberships tab. Right-click the desired Replicated Folder member and select Make Read-
only, as shown in Figure 28.26.
ptg
FIGURE 28.26
Converting a replicated folder to read-only.
As a best practice, when using read-only replicated folders, configure replication connec-
tions to be one-way to the read-only folder.
Enabling Access-Based Enumeration on a Domain-Based Namespace
in Windows Server 2008 Mode
When a domain-based namespace is created and Windows 2008 mode is enabled, access-
based enumeration can be enabled, but it is not by default. To enable access-based
enumeration on a domain-based namespace in Windows Server 2008 mode, locate the
Managing and Troubleshooting DFS
1163
namespace in DFS Management. Right-click the namespace and select Properties. Select
the Advanced tab and check the Enable Access-Based Enumeration for This Namespace
check box at the bottom of the window. Click OK to complete the change. One thing to
keep in mind is that this will apply to the entire namespace and any and all folders and
folder targets defined in the namespace.
Managing and Troubleshooting DFS
DFS can be managed through the DFS Management console included in the Windows
Server 2008 R2 Administrative Tools program group and in the Server Manager console.
DFS can also be managed in a command-line environment using the DFS command-line
utilities. These utilities include the following:
.
DfsUtil—
Can be used to manage DFS namespaces, servers, and clients. DfsUtil can
also be used to export DFS namespaces to XML files so they can be migrated to new
systems.
.
DfsCmd—
Can be used to manage the folders and targets within an existing DFS
namespace.
ptg
.
DfsrAdmin—
Can be used to perform actions on existing DFS Replication groups,
including adding new replication group folders and generating reports on existing
replicated folder members.
.
DfsrDiag—
Can be used to force replication, stop replication, or report on replica-
tion health.
Using the DFS management console, DFS standalone and domain-based roots can be
shown and managed in a single DFS console window. The administrator can check DFS
root and folder targets for availability by checking the Connection status of all targets for
28
a particular replication group. Using the DFS Management console, a DFS administrator
can also create a DFS Replication Diagnostic report. To create a diagnostic report for repli-
cation, perform the following steps:
1. Open the DFS Management console and expand it.
2. Double-click on Replication to reveal the desired replication group. If the desired
replication group is not shown, right-click the Replication node, select Add
Replication Groups to Display, and follow the steps to add the desired group.
3. Right-click the desired replication group, and select Create Diagnostic Report.