i bc27f85be50b71b1 (244 page)
Read i bc27f85be50b71b1 Online
Authors: Unknown


Consists of: a closed mask with a clear
to panicip3te m functional activities or an exercise
,.
soft gasket around Its border� placed
program. The unit may also be placed on a portable
:;
�
Z
over the nose to fit tightly 3gainst
mtravenous pole or cart for thiS purpose.
"
;::
the patient's face. Ir is held firmly m
place with straps around the top
and back of the head.
�
T rube/piece
Purpose: provide!l a specific concen
•
Patients who are weaning from a ventilator can [Ire
"
Fio.! _ 50-80%
tration of supplemental 02 to an
easily. Consult with the medical-surgical team to
2
mtubated, spontaneously breathing
determine whether the patient will tolerate ventilator
,
�
c:
patient while weaning from a
weaning (i.e., the use of a T piece) and physical
:c
<'
venti la tor.
therapy intervention simultaneously, or whether the
i;!
Consists of: a T-shaped tube attached
patient would benefit from bronchopulmonary
,...
directly to an endotracheal or trahygiene ro facil.tate weaning.
.0
c:
cheostomy tube. Humidified 02 is
�
delivered through one end of the T,
m
and expired gas exits the ocher end.
!i
The tubing acts as a reservoir for
z
02' allowing a specific concentra
:;!
'"
tion of 02 to be delivered.
,.
g
BiPAP = bilevel positive airway pressure; Fio2 = fraction of inspired oxygen; Ipm = liters per minute; 02 = oxygen; RA = room air.
'"
Sources: Data from RR Kirby, RW Taylor, JM Civetta (eds). Handbook of CfltlCal Care (2nd ed). Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1997; JM
\!
Rothstein (ed). The Rehabiluatlon SpecialiSt's Handbook (2nd cd). Philadelphia: FA DaVIS, 1998; and EF Ryerson, AJ Block. Oxygen as a Drug:
:c
m
Chmcal Propenies, Benefits, Modes and Hazards of Adminisnatlon. In GG Burton, JE Hodgkin (eds), Respiratory Care: A Guide to Clmical
�
Practice (3rd ed). Philadelphia: Llppmcotr, 1991.
�
Z
Cl
"
"
"

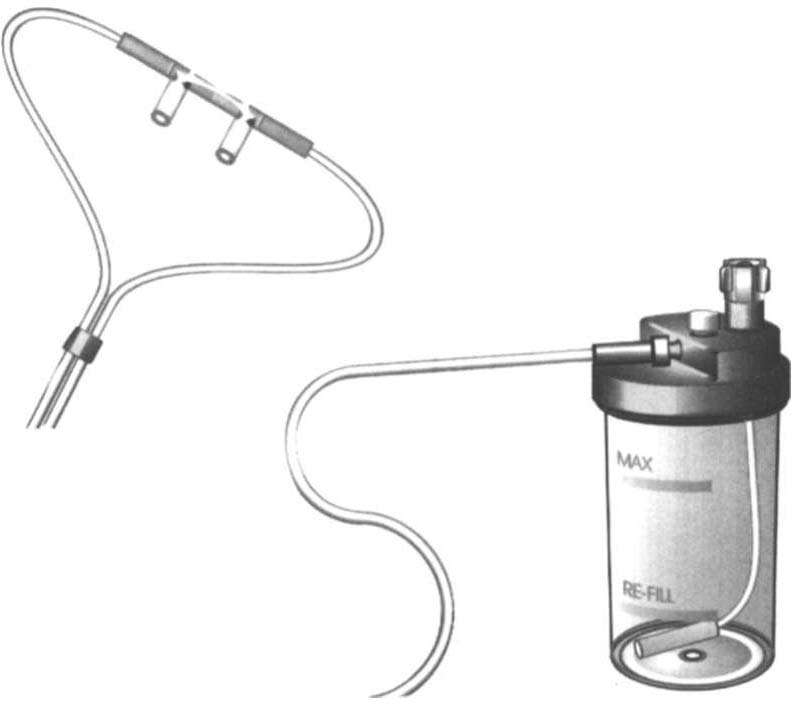
778 AClJTE CARE HANDBOOK FOR PHYSICAL THERA1'I5TS
Figure m-A.l. Nasal cannula with humidification. (Maersk Medical. Respiratory and Anesthesia Product Catalog. McAllen. TX.J
decrease in Pao2 originating in the aortic and carotid bodies." In theory, providing supplemental 02 may lead to a reduction in the hypoxic ventilatory drive. Apnea may result if chronic hypoxemia is
reversed with higher flows of supplemental 02' Potential respiratory
depression should never contraindicate oxygen therapy in severe
hypoxemia, however. If hypoventilation is a major problem, other
support measures, including mechanical ventilation, can be used.1
General Physical Therapy Considerations with
Oxygen Therapy
•
Note that a gree" label designates the 02 supply on hospital
walls. A similar gauge supplies pressurized air that is designated by
a yellow label.

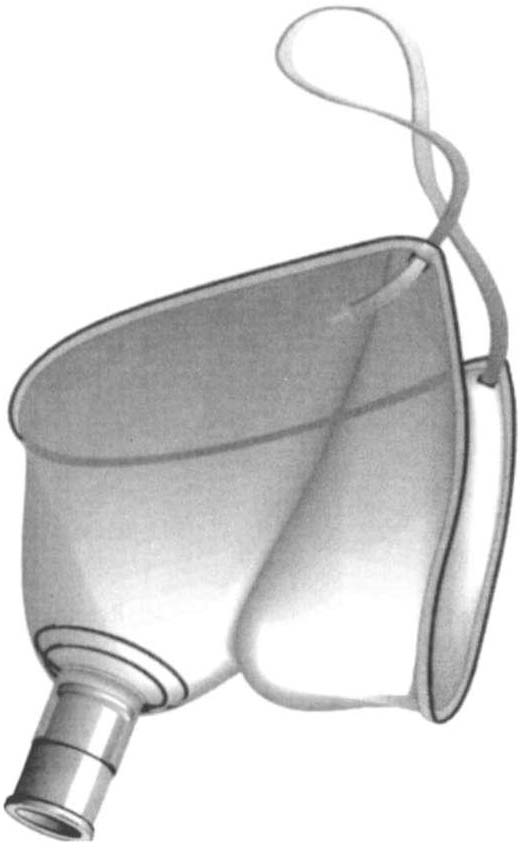
APPENDIX Ill-A: MEDICAl -SURGICAL EQUIPMENT IN THE AClITE CARE Sl:.TT1NG
779
Figure UI-A.2. Open (ace mask or tent. (Maersk Medical, Respiratory and
Anesthesia Product Catalog, McAllen, TX.J
•
Significant supplemental 0, requirements usually indicate a
respiratOry compromise, which in turn may indicate the need to
modify or defer physical therapy intervention.
•
Observe the patient for clinical signs of hypoxemia: shorrness of
breath, use of accessory muscles of breathing, confusion, pallor, or
cyanosis.
•
The Fio, for a given system is dependent on its proper fit and
application. Ensure that all connections are intact, that the 02 is


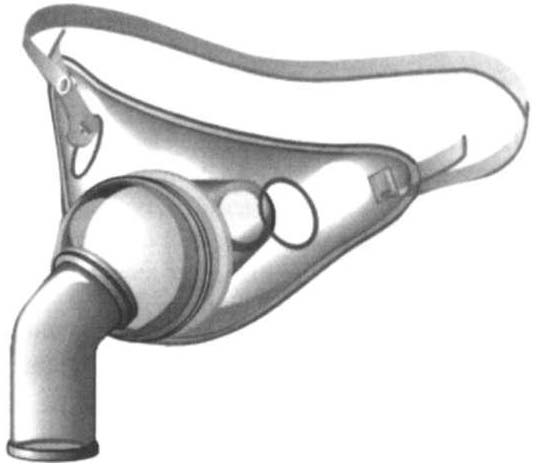
780
AClHE CARE HANDBOOK FOR I'HYSICAL THERAI'ISTS
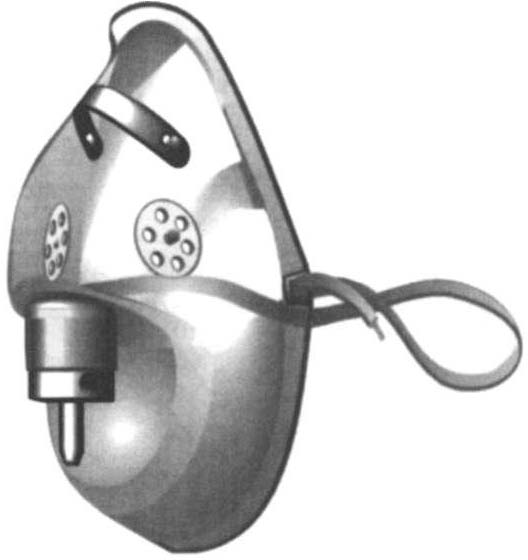
Figure m-A.3. Closed face mask. (Maersk Medical, Respiratory and Anesthesia Product Catalog, McAllen, TX.)
Figure JII-A.4. Tracheostomy mask or collar. (Maersk Medkal, Respiratory
and Anesthesia Product Catalog, McAllen, TX.)
