i bc27f85be50b71b1 (247 page)
Read i bc27f85be50b71b1 Online
Authors: Unknown
�
infarction, or before permanent pacemaker
However, the underlying indication for the
1::
placement. Refer to Management in Chapter
pacemaker may limit the patient's activiry
�
1 for morc information on pacemakers.
level. Check for mobility restrictions.
o
Consiscs of: pacing wires that connect to an
•
Temporary pacing wires should be kept dry.
g
external generator. There are three basic rypes.
•
Be aware of the location of the generator and
'"
Epicardial-the wires are placed after
wires at all times, especially during mobility
o
,.,
heart surgery on the epicardium and exit
activities.
�
through a mediastinal incision.
• If a temporary pacemaker is placed after a
:r
-<
�
Transvenous-the wires 3rc placed in the
coronary an:ery bypass graft (CABG), the wires
�
right ventricle via a central line.
art' usually removed 1-3 days after surgery. The
r
Transcutaneous-large elecrrodes 3rc
patient is usually placed on bed rest for 1 hr after
;!
placed on the skin over the anterior and
pacing wire removal, with vital sign monitoring
�
posterior chese.
every 15 mins.
�
�
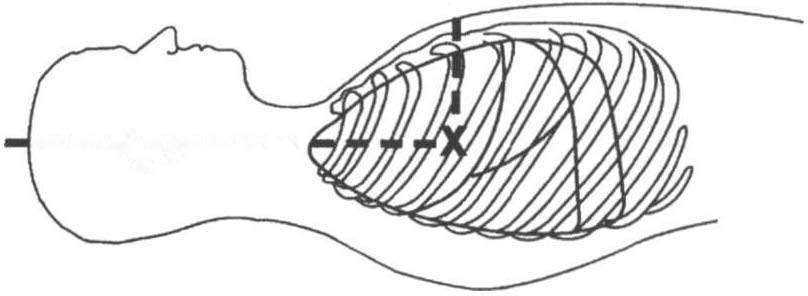
Pulmonary artery
Purpose: to dirocdy or indirocdy measure PAP,
• The patient with a PA line is usually on bed rest.
catheterization (PA line,
PAWP, LAP, RAP, CYP, core body
•
Avoid head and neck (for subclavian access) or
Swan-Ganz)
temperarure, CI, and CO in cases of
extremity movements that could disrupt the PA
Normal values: PAP
hemodynamic instabiliry, hean: failure, or
line at the insen:ion site, including the line
(mean), 10-20 mm Hg;
cardiogenic shock. Provides access to mixed
dressing.
PAWl' (mean), 6-12 mm
venous blood samples.
• PA\'(fP is an indirect measure of LAJ).
Hg; RAP, 0-8 mm Hg; core
Consists of: a multilumen catheter inserred
• PAP is equal to right ventricle pressure.
temperature, 98.2°-
through an introducing sheath into a large
• RAP is equal to CVP.
100.z°F (36.8°-37.9°C);
vein, usually the subclavian, or the
• CO equals stroke volume (SV) x hean: rate (HR).


CO, 4-5 Jpm; CI (COl
brachial, femoral. or inrernal jugular vein
>-
'"
body surface area), 3 Ipm!
(Figure III-A.9). The carherer is direcred by
'Z
012 for an average ISO·lb
blood flow into various locations of the
"
man
heart and pulmonary artery, with proper
x
placement confirmed by x-ray.
The catheter is connected to 3 transducer ro
<-
allow for continuous monitoring.
§
The proximal lumen opens into the right
n
>r
atrium to measure RAP and CO, and for
�
the delivery of fluids or medications.
'"
Cl
The distal lumen opens into the pulmonary
g
artery to measure PAP and PAWP.
r
To obtain a PAWP measurement, a balloon at
.2i
c
the end of the distal lumen is temporarily
'3
inflated. h follows the blood flow from the
3:
right ventricle into rhe pulmonary artery ro
2
a distal branch of the pulmonary artery,
z
where it is "wedged" for a short time (up
:;!
m
to 15 sees).
>-
A�line
�
= arterial line; CI = cardiac index; CO = cardiac Output; CVP = central venous pressure; LAP = left atrial pressure; Jpm = liters per minute; MAP = mean arterial pressure; PAP = pulmonary arrery pressure; PAWP = pulmonary artery wedge pressure; RAP = right atrial pressure.
r;?
Sources: Data from RR Kirby, RW Taylor, JM Civetta (cds). Handbook of Critical Care (2nd cd). Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1997; MR Kin�
'"
m
ney, SB Dunbar, JM Virello-Cicciu, et al. (cds). AACN's Clinical Reference for Critical Care Nursing (4rh cd). Sr. Louis: Mosby, 1998; EK Daily,JP
Schroeder. Clinical Management Based on Hemodynamic Parameters. In FJ( Daily, JP Schroeder (eds), Techniques in Bedside Hemodynamic Mon
�
itoring (5th ed). Sf. Louis: Mosby, 1994; and EJ Bridges. Moniroring pulmonary artery pressures: JUSt the facts. Crit Care Nurse 2000;2 1 (16):67.
Z
"
...,
00
'"


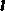
790 AClITE. CARE HANDBOOK FOR PHYSICAL THERAPISTS
PHLEBOSTATIC AX'S
4ICS
I
-- � ---
Mid-Point
A-P Chest Wall
Figure m-A.7. The phlebostatic axis at the intersection of the fourth intercostal space (lCS) and the midpoint of the anterior (A) and posterior (P) chest wall. (Reprinted with permission from Edwards Lifesciences LLC.)
Aorta
Radial artery
Dorsalis pedis artery
lime
Figure ID-A.8. Arteria/line tracing from different sites. (Repri"ted with permission from SM Yent;s, NP Hirsh, GB Smith leds/, Anaesthesia and Intensive Care A-Z. An Encyclopedia of Principles and Practice 12nd edJ. Oxford, UK: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2000;45.)
